Spegazzinia deightonii
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Samarakoon2020MycoKeys70, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Samarakoon2020MycoKeys70">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Pleosporales
Familia: Didymosphaeriaceae
Genus: Spegazzinia
Name
Spegazzinia deightonii (S. Hughes) Subram., J. Indian bot. Soc. 35: 78 (1956) – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Description
Saprobic on dead leaves of Musa sp. Sexual morph Undetermined. Asexual morph Hyphomycetous. Sporodochia powder like, dark, dense, dry, 1–3 mm diameter. Conidiophore mother cells 3.5–6.8 × 2.5–5.0 μm (x̄ = 5.59 × 4.15 μm, n = 6), hyaline to light brown, subspherical or doliiform. Conidiophores long or short and give rise to two types of conidia referred here as α and β. Conidiophores of α conidia up to 48–120 × 1–2 μm (x̄ = 95.3 × 1.6 μm, n = 20) long, erect or flexuous, narrow, verruculose, unbranched, hyaline to golden-brown. Conidiophores of β conidia initially hyaline, light brown to brown at maturity, very short and slightly bent, 1.6–2 × 2.5–3 μm (x̄ = 1.8 × 2.6 μm, n =10). Conidiogenous cell development basauxic, forming a single, terminal holoblastic conidium at the apex of conidiophore. Conidial development holoblastic. Conidia two types: α conidia stellate, 18–28 × 17–29 μm (x̄ = 25.1 × 23.3 μm, n = 25), solitary, globose to variously shaped, with spines 4–6 μm long, 4–8-celled, frequently 4- to 6-celled, deeply constricted at the septa. β conidia disc-shaped, initially hyaline, light brown to dark brown at maturity, 8-celled, 16–21 × 11–14 μm (x̄ = 19.2 × 14.6 μm, n = 25), flat from both sides with short and blunt spines, frequently with attached conidiogenous cells when splitting from the conidiophores.
Culture characteristics
Conidia germinating on PDA within 13–14 h. Colonies growing on PDA, reaching a diameter of 55 mm after 14 d at 25 °C, raised, moderately dense, undulate margin, middle grey, periphery brownish grey and olive green at immature stage; reverse white to greyish white.
Material examined
Thailand, Chiang Rai Province, Doi Thun, on a dead leaf of Musa sp. (Musaceae), 7 December 2018, M.C. Samarakoon, BNS 072 (MFLU 19-2908), living culture MFLUCC 20-0002.
Notes
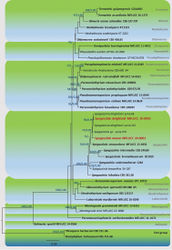
Spegazzinia deightoniiMFLUCC 20-0002 clustered with S. deightonii (yone 66, yone 212) with significant statistical support (Figure 1). All the strains of S. deightonii described in Ellis (1971)[1] and Tanaka et al. (2015)[2] have similar morphological features with our strain such as dark brown, 8-celled, disked-shaped, spiny conidia. With morphological and multigene phylogenetic support, we report a new host record of S. deightonii from Musa sp.
Taxon Treatment
- Samarakoon, B; Phookamsak, R; Wanasinghe, D; Chomnunti, P; Hyde, K; McKenzie, E; Promputtha, I; Xu, J; Li, Y; 2020: Taxonomy and phylogenetic appraisal of Spegazzinia musae sp. nov. and S. deightonii (Didymosphaeriaceae, Pleosporales) on Musaceae from Thailand MycoKeys, 70: 19-37. doi
Images
|
Other References
- ↑ Ellis M (1971) Dematiaceous hyphomycetes. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew.
- ↑ Tanaka K, Hirayama K, Yonezawa H, Sato G, Toriyabe A, Kudo H, Hashimoto A, Matsumura M, Harada Y, Kurihara Y, Shirouzu T (2015) Revision of the Massarineae (Pleosporales, Dothideomycetes). Studies in mycology 82: 75–136. ttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.simyco.2015.10.002