Malagasyprinus
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Lackner2013ZooKeys333, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Lackner2013ZooKeys333">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Coleoptera
Familia: Histeridae
Name
Malagasyprinus Lackner & Gomy, 2013 gen. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Type species
Saprinus caeruleatus Lewis, 1905.
Diagnosis
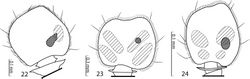
Rather small Saprininae histerid (PEL 2.05–2.60 mm) with black body, brown to black elytra; dorsally with blue metallic tinge; legs and antennae paler than the rest. Frons rugulose-lacunose, coarsely and densely punctured, depressed; frontal stria widely interrupted anteriorly, prolonged onto clypeus, sometimes difficult to discern and appearing complete; sensory structures of antenna in form of a single sensory area with a corresponding stipe-shaped vesicle situated on internal distal side of the antennal club (Fig. 22); eyes large and strongly convex; pronotal hypomeron asetose; pronotal foveae (sensu Lackner 2010[1]: 38, fig. 146) absent, pronotum with variously deep longitudinal lateral depression separated from the pronotal margin by a slightly convex punctate band, median part of pronotum moderately to strongly convex, entire pronotal disc with coarse punctures, lateral longitudinal depression and surface around it with extremely rugose and deep longitudinal wrinkles; marginal pronotal stria carinate laterally, slightly bi-sinuate; entire elytral disc (with exception of small, occasionally punctate ‘mirror’ on fourth elytral interval) coarsely verrucose-punctate; dorsal elytral striae obliterated by punctuation, represented occasionally only by their basal fragments; basal fragment of fourth dorsal elytral stria and basal third to half of sutural elytral stria present as a rule, connected; humeral elytral stria usually discernible. Prosternal foveae (pre-apical foveae of Lackner 2010[1]: 41, fig. 148) large and deep; both sets of prosternal striae present; prosternal process in two species depressed on anterior two-thirds; underside of the body with variously coarse and dense punctuation (depending on species).
Differential diagnosis
Externally this new taxon at first glance resembles a specimen of the genus Saprinus s. str. (the type species of this genus has originally been a Saprinus), but the shape of the sensory structures of the antenna should distinguish it from Saprinus immediately (compare Figs 22 and 23). Furthermore, the deep longitudinal pronotal wrinkled depression with convex median part of the pronotum, and large and deep prosternal foveae quickly separate it from the members of Saprinus as well. However, prosternal foveae are present among the members of the primarily Palaearctic subgenus Hemisaprinus Kryzhanovskij in Kryzhanovskij and Reichardt 1976 of the genus Saprinus Erichson, 1834 but they are never as deep and large as in this newly erected genus, and, furthermore, the pronotal depressions (pronotal foveae of Lackner 2010[1]: 38, fig. 146) are present in Hemisaprinus, whereas they are absent in Malagasyprinus. The most marked differences between Hemisaprinus and Malagasyprinus are found in the structure of their sensory areas of the antenna: the sensory structures of the antennal club of the type specimen of the subgenus Hemisaprinus, Saprinus (Hemisaprinus) subvirescens (Ménétriés, 1832) are similar to those of Saprinus semistriatus, and consist of four ovoid sensory areas on ventral side and one vesicle situated under internal distal margin (compare Figs 22 and 24). In order to distinguish this newly erected genus from other Afrotropical genera, the reader is referred to the key by the senior author (Lackner 2013[2]: 66). Although this key features only the species “Saprinus caeruleatus”, it is well applicable for all members of Malagasyprinus.
Biology
Series of Malagasyprinus caeruleatus comb. n. have been collected in a dry forest by a pitfall trap baited with fish. Specimens of Malagasyprinus perrieri sp. n. and Malagasyprinus diana sp. n. have been collected by beating the bushes, as well as by pitfall traps.
Distribution
Madagascar.
Etymology
The name of this newly erected taxon is a combination of the genus name Saprinus with a prefix derived from the epithet suggesting Madagascar origin. Gender masculine.
Original Description
- Lackner, T; Gomy, Y; 2013: Malagasyprinus, a new genus of the Saprininae from Madagascar with description of two new species (Coleoptera, Histeridae, Saprininae) (First contribution to the knowledge of the Histeridae of Madagascar) ZooKeys, 333: 55-76. doi
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lackner T (2010) Review of the Palaearctic genera of Saprininae (Coleoptera: Histeridae). Acta Entomologica Musei Nationalis Pragae 50 (Supplementum): 1–254.
- ↑ Lackner T (2013) Afroprinus cavicola gen. et sp. n. from the Afrotropical region with notes on cave-dwelling Saprininae (Coleoptera: Histeridae). Zookeys 294: 57-73. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.294.4800
Images
|