Sinosmylites fumosus
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Makarkin2011ZooKeys130, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Makarkin2011ZooKeys130">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Neuroptera
Familia: Berothidae
Genus: Sinosmylites
Name
Sinosmylites fumosus Makarkin & Yang & Ren, 2011 sp. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Diagnosis
Differs from Sinosmylites pectinatus by CuP once forked (twice forked in Sinosmylites pectinatus), by presence of one ‘inner’ gradate series of crossveins (two in Sinosmylites pectinatus) (see differences from Sinosmylites rasnitsyni sp. n. under that species.).
Description
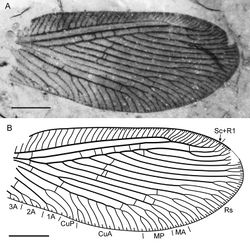
Forewing with broad-rounded apex, about 6.0 mm long (as preserved, estimated complete length about 6.5 mm), 2.6 mm wide. Costal space moderately broad, most dilated at proximal 1/5 of wing length. Subcostal veinlets simple, regularly arranged, less closely spaced than in previous species. Sc distally fused with R1 far from wing apex; Sc+R1 with nine veinlets (eight simple, one forked). Subcostal space broad, with two basal crossveins. R1 space nearly as wide as subcostal space; six crossveins before fusion of Sc and R1, one after. Rs with nine pectinate, regularly spaced branches; four proximal-most branches with 2-4 terminal forks, other branches once forked. Rs1 originating at some distance from origin of Rs. M not fused basally; forked much distal to origin of Rs1. MA, MP almost parallel, distally with one (simple) , two (one simple) branches respectively. Cu divided into CuA, CuP proximal to origin of Rs. CuA pectinate, with 7 branches; proximal-most branch once forked. CuP once deeply forked. Anal veins incompletely preserved; 1A with single marginal fork; 2A with two marginal short branches; 3A very incomplete, with single fork preserved. Four gradate series of crossveins posterior to stem of Rs, all incomplete. First series consists of three crossveins: 1r-m (located at origin of Rs), 1m-cu, 1a1-a2 (longer than previous); Second series includes two crossveins: 2m-cu (connecting MP, CuA), 2icu (connecting CuA, anterior branch of CuP). Third (‘inner’) series with six crossveins (3rs-rs7, 3rs5-rs4 to 3rs2-rs1; two between Rs3, Rs2). Fourth (‘outer’) series with five crossveins (from 4rs2-rs1 to 4m-cu; two between Rs1, MA). Wing one color, fuscous. Veins mainly dark brown as preserved.
Type material
Holotype CNU-NEU-NN2011003, deposited in CNUB. A nearly complete forewing.
Type locality and horizon
Daohugou Village, Shantou township, Ningcheng county, Inner Mongolia, China. Jiulongshan Formation, Middle Jurassic.
Etymology
From the Latin fumosus, smoked, in reference to the coloration of wings.
Original Description
- Makarkin, V; Yang, Q; Ren, D; 2011: Two new species of Sinosmylites Hong (Neuroptera, Berothidae) from the Middle Jurassic of China, with notes on Mesoberothidae ZooKeys, 130: 199-215. doi
Images
|