Pseudamnicola astieri
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Delicado2012ZooKeys190, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Delicado2012ZooKeys190">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Sorbeoconcha
Familia: Hydrobiidae
Genus: Pseudamnicola
Name
Pseudamnicola astieri (Dupuy, 1851) – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Hydrobia astierii Dupuy, 1851: 556–557, pl. XXVII, fig. 12, Paris (Type loc. surroundings of Grasse, Alpes-Maritimes, France [shell description]).
- Paludinella astieri (Dupuy): Frauenfeld 1865[1]: 575.
- Bythinella astieri (Dupuy): Locard 1882[2]: 227; Bérenguier 1882[3]: 83; Locard 1893[4]: 79, fig. 81 (shell description); Berenguier 1902: 378, pl. 16 fig. 6 (1990).
- Bythinella anteisensis Bérenguier, 1882: 83, 89–90 (Type loc. Foux de Draguignant, Var, France [shell description]); Bérenguier 1902[5]: 378–379 (shell description) pl. 16 fig. 7 (1990). (Synonymy: Girardi 2009[6]: 56).
- Bythinella berenguieri Bourguignat in Bérenguier, 1882: 83, 99–100 (Type loc. Foux de Draguignant, Var, France [shell]); Bérenguier 1902[5]: 379–380 (shell description) pl. 16 fig. 8 (1990) (Synonymy: Girardi 2009[6]: 56).
- Bythinella doumeti Bourguignat in Locard, 1893: 91. (Type loc. surroundings of Nimes, Gard, France [shell description]) (Synonymy: Falkner et al. 2002[7]: 81, after revision of two syntypes in the Bourguignat collection, MHNG).
- Corrosella anteisensis (Bérenguier): Boeters, 1970: 64, figs. 2, 4, 7, 9 [(shell, operculum, male and female genital systems of topotypes; Boeters could not find the syntypes)], (=Bythinella berenguieri Bourguignat in Bérenguier). (Synonymy: Girardi 2009[6]: 56).
- Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astierii (Dupuy): Falkner et al. 2002[7]: 29, 80-81;Girardi 2009[6]: 56–61, figs. 1–3 (Var, France: Source d’Argens, Source du Pavillon, Source de la Foux à Draguignan [shell and anatomy]).
Type locality
Surroundings of Grasse, France (Dupuy, 1851).
Type material
Boeters (1970)[8] reported the existence of one specimen with the label “Paludinella astieri, typus ex Dupuy” in Paladilhe’s collection at the Faculté des Sciences, Montpellier, France. We tried in vain to confirm the existence of such material at the university mentioned. Consequently, we should consider that the type specimen is presently inaccessible for study. However, some topotypes of Corrosella anteisensis (Bérenguier) from Foux à Draguignan, Var exist: BOE 261, 285 a-c, 291b Boeters (1970)[8] and Girardi (2009)[6]. This author also reported Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri from Source d’Argens, Brue-Aurillac à Seillons, Var and the Source du Pavillon, Ruisseau Fauvery à Pontevès, Var (Girardi 2009[6]).
Material examined
A few specimens collected from Source d’Argens , Brue-Aurillac, Var, France after finding the type area and other localities in Alpes-Maritimes and Var practically destroyed by severe storms. A total of two females and four males have been examined for anatomical descriptions.
Localities
Source d’Argens, Brue-Aurillac, Var, France, 43°30.24'N, 5°54.43'E, D.D., 21 June 2010, MNCN 15.05/60025 (70° ethanol, Figures 2–4) and MNCN/ADN 54949–54951 (absolute ethanol). For more localities, see Girardi 2009[6].
New diagnosis
Shell yellowish or whitish with a body whorl occupying 2/3 shell length and a deep suture between whorls; protoconch microsculpture granulated; central radular tooth formula 7-C-7; style sac surrounded by a black pigmented intestine; elongate bursa copulatrix U-shaped; elongate seminal receptacle without duct; penis slender with a black patch of pigmentation and some folds in its middle region; nervous system brown pigmented with supraoesophageal connective about two times longer than suboesophageal.
Description
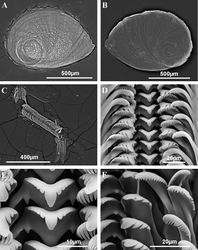
Shellovate-conic with 4–4.75 spire whorls, height 2.5–3.5 mm (Figure 2A–C; Table 2); periostracum yellowish or whitish; protoconch approximately 370 µm wide with 1.5 whorls and a nucleus around 150 µm long (Figure 2D, E); protoconch microsculpture granulated, more intense on apex (Figure 2E); body whorl about 2/3 total length; teleoconch whorls convex with a deep suture; peristome orthocline; aperture complete, oval, with an inner lip thicker than outer lip; peristome margin simple, straight (Figure 2B).
| Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri (n=11) |
Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (n=18) |
T-test (p values) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | ||
| SL | 3.11 (3.56–2.58) |
0.25 | 0.08 | 2.50 (2.85–2.17) |
0.18 | 0.07 | p < 0.001 |
| SW | 1.92 (2.28–1.74) |
0.15 | 0.08 | 1.59 (1.78–1.44) |
0.10 | 0.06 | p < 0.001 |
| SL/SW | 1.62 (1.76–1.45) |
0.10 | 0.06 | 1.57 (1.73–1.46) |
0.07 | 0.04 | n.s. |
| AH | 1.37 (1.78–1.26) |
0.14 | 0.10 | 1.20 (1.36–1.04) |
0.08 | 0.07 | p < 0.001 |
| SL–LBW | 1.10 (1.39–0.76) |
0.16 | 0.15 | 0.69 (1.00–0.49) |
0.13 | 0.19 | p < 0.001 |
| WBW | 1.76 (1.89–1.59) |
0.09 | 0.05 | 1.42 (1.57–1.29) |
0.07 | 0.05 | p < 0.001 |
| AL | 1.39 (1.72–1.28) |
0.12 | 0.08 | 1.26 (1.41–1.11) |
0.09 | 0.07 | p < 0.01 |
| AW | 1.01 (1.33–0.85) |
0.14 | 0.14 | 0.89 (1.11–0.78) |
0.08 | 0.09 | p < 0.01 |
| WPW | 1.23 (1.33–1.11) |
0.08 | 0.07 | 0.95 (1.12–0.80) |
0.08 | 0.08 | p < 0.001 |
| WAW | 0.19 (0.32–0.15) |
0.06 | 0.32 | 0.28 (0.37–0.19) |
0.04 | 0.14 | p < 0.001 |
| NSW | 4.30 (4.75–4.00) |
0.31 | 0.07 | 4.18 (4.50–4.00) |
0.21 | 0.05 | n.s. |
| Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri (n=5) | Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (n=7) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Max-Min) | SDN | CV | Mean (Max-Min) | SDN | CV | |
| OL | 1.10 (1.18–0.96) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 1.08 (1.18–0.96) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| OW | 0.79 (0.84–0.73) | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.74 (0.84–0.66) | 0.06 | 0.08 |
| OLWL | 0.48 (0.56–0.40) | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.49 (0.63–0.36) | 0.08 | 0.17 |
| OLWW | 0.34 (0.40–0.25) | 0.05 | 0.16 | 0.33 (0.38–0.29) | 0.03 | 0.09 |
| NL | 0.47 (0.52–0.39) | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.36 (0.44–0.26) | 0.06 | 0.17 |
| NW | 0.36 (0.42–0.31) | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.29 (0.45–0.21) | 0.06 | 0.22 |
|+ Table 4. Radula formulae and measurements (in mm) of three radulae of Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri from d’Argens spring, Seillons, France and three of Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. from Los Nogales spring, Benafer, Castellón, Spain. |- ! !! Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri !! Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. |- | Central teeth || 7+C+7/1–1 || 5+C+5/1–1 |- | Central teeth width || ~ 20 µm || ~ 15 µm |- | Lateral teeth || 3–C–3 || 3–C–3 |- | Inner marginal teeth || ≥ 18 cusps || ≥ 15 cusps |- | Outer marginal teeth || ≥ 19 cusps || ≥ 19 cusps |- | Radula length || ~ 700 µm || ~ 600 µm |- | Radula width || ~ 90 µm || ~ 95 µm |- | Number of rows || ~ 55 || ~ 50 |} Pigmentation and anatomy: Head dark brown pigmented from snout to neck (Figure 4D); pigmentation clearer on neck; tentacles also brown pigmented except for a narrow band on these and on ocular lobes; snout long as wide, with medial lobation; foot intermediate length and pigmented in dorsal region. Ctenidium in middle region of pallial cavity filling ca. 70% of its length with 17–18 gill filaments; osphradium intermediate width under central gill filaments (Figure 4C, Table 5). Stomach slightly longer than wide with a small posterior caecum; style sac shorter than stomach and surrounded by intestine black pigmented (Figure 4F, Table 5).
| Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri (n=5) |
Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (n=7) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | |
| Ct L | 1.06 (1.25–0.90) |
0.15 | 0.14 | 1.11 (1.27–0.92) |
0.16 | 0.14 |
| Os L | 0.32 (0.43–0.20) |
0.09 | 0.27 | 0.33 (0.45–0.24) |
0.07 | 0.22 |
| Os W | 0.13 (0.15–0.11) |
0.02 | 0.16 | 0.21 (0.25–0.15) |
0.03 | 0.15 |
| Ss L | 0.59 (0.67–0.50) |
0.06 | 0.11 | 0.62 (0.66–0.58) |
0.03 | 0.05 |
| Ss W | 0.35 (0.37–0.31) |
0.02 | 0.06 | 0.37 (0.41–0.33) |
0.03 | 0.08 |
| St L | 0.71 (0.74–0.66) |
0.04 | 0.06 | 0.73 (0.84–0.66) |
0.06 | 0.09 |
| St W | 0.61 (0.67–0.56) |
0.04 | 0.07 | 0.69 (0.78–0.61) |
0.06 | 0.09 |
| Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri | Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | |
| Po L | 2.22 (2.35–2.08) |
0.24 | 0.11 | 2.04 (2.32–1.75) |
0.26 | 0.13 |
| Po W | 0.58 (0.59–0.56) |
0.03 | 0.04 | 0.45 (0.49–0.41) |
0.04 | 0.10 |
| Ag. L | 0.95 (1.04–0.84) |
0.18 | 0.18 | 0.81 (1.00–0.71) |
0.14 | 0.17 |
| Cg. L | 1.01 (1.11–0.91) |
0.18 | 0.17 | 1.00 (1.11–0.93) |
0.09 | 0.09 |
| SR1 L | 0.14 (0.15–0.14) |
0.01 | 0.09 | 0.18 (0.22–0.15) |
0.03 | 0.18 |
| BC L | 1.24 (1.32–1.15) |
0.15 | 0.12 | 1.37 (1.56–0.95) |
0.30 | 0.22 |
| BC W | 0.30 (0.35–0.25) |
0.09 | 0.29 | 0.31 (0.36–0.25) |
0.05 | 0.18 |
| dBC L | 0.60 (0.75–0.65) |
0.09 | 0.15 | 0.62 (0.72–0.46) |
0.13 | 0.21 |
| Pr L | 1.67 (1.86–1.55) |
0.14 | 0.08 | 1.37 (1.46–1.26) |
0.09 | 0.06 |
| Pr W | 0.58 (0.69–0.52) |
0.09 | 0.15 | 0.45 (0.51–0.41) |
0.05 | 0.12 |
| P L | 1.26 (1.35–1.15) |
0.09 | 0.07 | 1.28 (1.60–1.12) |
0.24 | 0.19 |
| P W | 0.37 (0.40–0.33) |
0.03 | 0.09 | 0.66 (0.75–0.50) |
0.12 | 0.18 |
| PL/Head length | 1.02 (1.16–0.86) |
0.16 | 0.16 | 0.91 (1.07–0.82) |
0.15 | 0.17 |
Nervous system brown pigmented, consisting of disperse points of pigmentation; cerebral ganglia equal in size; supraoesophageal connective more than two times longer than suboesophageal (Figure 4A, B; Table 7). Mean RPG ratio 0.42 (moderately concentrated).
| Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri (n=5) |
Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (n=5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | Mean (Max-Min) |
SDN | CV | |
| LRCG | 0.22 (0.24–0.20) |
0.02 | 0.10 | 0.21 (0.23–0.18) |
0.02 | 0.10 |
| LLCG | 0.22 (0.25–0.18) |
0.03 | 0.15 | 0.22 (0.24–0.19) |
0.02 | 0.10 |
| LCC | 0.11 (0.12–0.07) |
0.02 | 0.19 | 0.15 (0.19–0.12) |
0.02 | 0.14 |
| LRPG | 0.13 (0.18–0.10) |
0.03 | 0.25 | 0.15 (0.16–0.12) |
0.02 | 0.14 |
| LLPG | 0.17 (0.20–0.13) |
0.03 | 0.19 | 0.23 (0.28–0.20) |
0.03 | 0.14 |
| LsupG | 0.14 (0.17–0.11) |
0.03 | 0.23 | 0.12 (0.15–0.10) |
0.02 | 0.18 |
| LsubG | 0.11 (0.13–0.09) |
0.01 | 0.10 | 0.12 (0.14–0.09) |
0.02 | 0.18 |
| LPsupC | 0.18 (0.24–0.11) |
0.05 | 0.30 | 0.29 (0.39–0.21) |
0.07 | 0.26 |
| LPsubC | 0.07 (0.09–0.06) |
0.01 | 0.15 | 0.10 (0.13–0.05) |
0.03 | 0.32 |
| RPG | 0.40 (0.49–0.38) |
0.05 | 0.13 | 0.51 (0.58–0.46) |
0.05 | 0.10 |
Remarks
The only available information on the anatomy of this species in the literature corresponded to populations from Foux à Draguignan (figure 2, 4, 7, 9 in Boeters 1970[8] and figure 2 by M. Bodon in Girardi 2009[6]) and Source du Fauvery in Pontevès (figure 1 by M. Bodon in Girardi 2009[6]). The specimens examined from Source d’Argens (Brue-Aurillac) are similar in shell and gastric complex shapes to specimens from Source du Fauvery though they more resemble specimens from the Foux à Draguignan in terms of pallial oviduct shape and number of gill filaments. However, other important diagnostic characters such as the shape of the penis and bursa copulatrix as well as seminal receptacle shape and its position on the renal oviduct are similar in the three populations. Based on these comparisons we conclude that specimens of the three localities belong to the same taxonomic unit with some inter-population variability shown.
Comparingshell sizes among the Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) species from the northern half of Iberian Peninsula, the shells of Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri are larger (2.5–3.5 mm) than those of Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (2.20–2.90 mm) (see statistically significant differences in shell measurements in Table 2) and Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hinzi Boeters, 1986[9] (2.2–2.7 mm, Boeters 1986[9]) yet similar in size to those of Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) navasiana (Fagot, 1907) (3.0–3.5 mm, Boeters 1988[10]). The only two shell variables resulting no significant between Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri and Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. were the rate SL/SW and NSW. That means that both species share the same ovate-conic shape and around 4 spire whorls, which are common characteristics among all Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) species. Anatomically, Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri bears a similar or higher number of gill filaments (about 17–18) than Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hinzi (16–17, Boeters 1986[9]), Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) navasiana (15–16, Boeters 1988[10]) and Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. (about 15). The penis in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri is narrower and more slender than in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n. and Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) navasiana, although it is wider and longer than in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hinzi. The copulatory organ is pigmented in its distal region in all four species, but the pigmentation patch is larger in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri. Although the bursa copulatrix is usually elongate or pyriform shaped among (Pseudamnicola) Corrosella species, it is U-shaped and folded in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astieri whereas it is J-shaped in Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hauffei sp. n., Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) hinzi and Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) navasiana. A small seminal receptacle (around 0.15 mm) is a character common to all four species.
Taxon Treatment
- Delicado, D; Ramos, M; 2012: Morphological and molecular evidence for cryptic species of springsnails [genus Pseudamnicola ( Corrosella) (Mollusca, Caenogastropoda, Hydrobiidae)] ZooKeys, 190: 55-79. doi
Other References
- ↑ Frauenfeld G (1865) Verzeichniss der Namen der fossilen und lebenden Arten der Gattung Paludina (Lam.) nebst jenen der näckststehendeu und Eiureihung derselben in die verschiedenen neueren Gattungen. Verhandlungen der Zoologisch-Botanischen Gesellschaft in Wien XIV: 562–672.
- ↑ Locard A (1882) Catalogue general mollusques vivants de France: Mollusques terrestres, des eaux douces et des eaux salmastres. H. Georg, Lyon, 462 pp.doi: 10.5962/bhl.title.10669
- ↑ Bérenguier P (1882) Essai sur la faune malacologique du departement de Var. Société d’études scientifiques et archéologiques de Draguignan, France, 131 pp.
- ↑ Locard A (1893) Les coquilles des eaux douces et saumâtres de France. B Baillière, Paris, 327 pp.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Bérenguier P (1902) Malacographie du Département du Var. C. et A. Latil, Draguignan, 540 pp.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Girardi H (2009) Pseudamnicola (Corrosella) astierii (Dupuy, 1851), dans les eaux de Var, France (Mollusca: Caenogastropoda: Hydrobiidae). Documents malacologiques 3: 56-61.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Falkner G, Ripken T, Falkner M (2002) Mollusques continentaux de France. Liste de Reférénce annotée et bibliographie. Patrimoines Naturels 52, 350 pp.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Boeters H (1970) Corrosella n. gen. (Prosobranchia: Hydrobiidae). Journal de Conchiliologie 108 (3): 63-69.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Boeters, H (1986) Unbekannte westeuropäische Prosobranchia, 7. Heldia 1 (4): 125-128.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Boeters H (1988) Moitessieriidae und Hydrobiidae in Spanien und Portugal. Archiv für Molluskenkunde 118(4/6): 181–261.
Images
|