Monodius
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Kamiński2014ZooKeys415, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Kamiński2014ZooKeys415">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Coleoptera
Familia: Tenebrionidae
Name
Monodius Koch, 1956 stat. r. – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Type species
Selinus convexipennis Gebien, 1904; by original designation.
Diagnosis
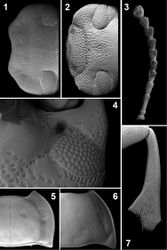
The following character combination is unique for Monodius within the whole subtribe Platynotina: (1) antennomeres from 7 to 11 elongated (their length greater than the width), (2) anterior tentorial pit deep, clearly visible, (3) 5th abdominal ventrite strongly widened, (4) female protarsi widened, (5) penis wide, at least 4 times wider than clavae, (6) clavae long, their length more than half of the length of parameres, (7) apex of parameres fused and (8) bursa copulatrix with 2 additional sacs.
Distribution
Monodius specimens have been collected in the following ecoregions of West and Central Africa (Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Federal Republic of Nigeria, Ivory Coast, Republic of Benin, Republic of Ghana, Republic of Liberia, Republic of Niger, Sierra Leone, Togolese Republic): Cross-Sanaga-Bioko coastal forests, Atlantic Equatorial coastal forests, Central African mangroves, Eastern Guinean forests, Guinean forest-savanna mosaic, Mount Cameroon and Bioko montane forests, Northern Congolian forest-savanna mosaic, Northwestern Congolian lowland forests, West Sudanian savanna, Western Guinean lowland forests (Figs 42–43).
Species included (7)
Monodius convexipennis (Gebien, 1904), Monodius gravis Koch, 1956, Monodius laevistriatus (Fairmaire, 1897), comb. n., Monodius lamottei (Gridelli, 1954), comb. n., Monodius malaisei Koch, 1956, Monodius medius (Fairmaire, 1897), Monodius plicicollis (Fairmaire, 1897), comb. n.
Key to the species of Monodius
Taxon Treatment
- Kamiński, M; 2014: A cladistically based reinterpretation of the taxonomy of two Afrotropical tenebrionid genera Ectateus Koch, 1956 and Selinus Mulsant & Rey, 1853 (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae, Platynotina) ZooKeys, 415: 81-132. doi
Other References
- ↑ Iwan D (2001b) Comparative study of male genitalia in Opatrinae sensu Medvedev (1968) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), with notes on the tribal classification. Part I. Annales Zoologici 51: 351–390.
- ↑ Iwan D (2002a) Generic classification of the tribe Platynotini (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), with notes on phylogeny. Annales Zoologici 52: 1–149.
Images
|
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Olson D, Dinerstein E, Wikramanayake E, Burgess N, Powell G, Underwood E, D’Amico J, Itoua I, Strand H, Morrison J, Loucks C, Allnutt T, Ricketts T, Kura Y, Lamoreux J, Wettengel W, Hedao P, Kassem K (2001) Terrestrial Ecoregions of the World: A new map of life on Earth (PDF, 1.1M). BioScience 51: 933–938. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0933:TEOTWA]2.0.CO;2


![Figure 42. Distribution of the species of Monodius convexipennis, Monodius gravis, Monodius laevistriatus, Monodius lamottei and Eleoselinus gen. n. The division of Afrotropical Realm into ecoregions was adopted after Olson et al. 2001[1]. Different colors were used to distinguish the adjacent ecoregions.](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=Zookeys-415-081-g010.jpg&width=250)
![Figure 43. Distribution of the species of Monodius malaisei, Monodius medius and Monodius plicicollis. The division of Afrotropical Realm into ecoregions was adopted after Olson et al. 2001[1]. Different colors were used to distinguish the adjacent ecoregions.](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=Zookeys-415-081-g011.jpg&width=250)
