Megachile gentilis
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Bzdyk2012ZooKeys221, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Bzdyk2012ZooKeys221">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Hymenoptera
Familia: Megachilidae
Genus: Megachile
Name
Megachile gentilis Cresson, 1872 – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Megachile gentilis Cresson, 1872: 267. Holotype male, USA: Texas (ANSP).
- Megachile palmarum Perkins, 1899: 114. Syntypes male female, USA: Hawaii (Repository?).
- Megachile murinella Cockerell, 1908: 263. Holotype female, USA: New Mexico (USNM).
Diagnosis
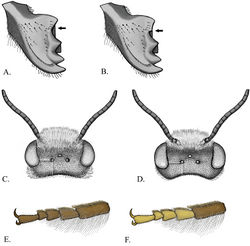
Megachile gentilis closely resembles Megachile mendica. The males of the two species can only be separated by two characters. In Megachile gentilis, the punctures on T6 are nearly contiguous creating the appearance of small ridges, with shiny surface almost completely obscured, and T2 has an apical fringe of white hair, while the fringe is absent in Megachile mendica. The females are slightly easier to differentiate. Megachile gentilis has a very slightly concave S6, with black pubescence and some erect setae basally. Megachile mendica has brown appressed pubescence and no erect setae. Also, Megachile gentilis has black scopal setae on S6 and basally on S5, while Megachile mendica has black setae only apically on S6. Megachile gentilis females also resemble Megachile coquilletti females. These can be differentiated by the angulate mandible of Megachile gentilis (Figure 4B).
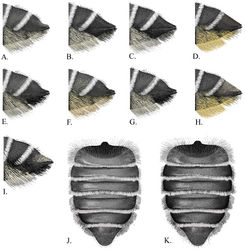
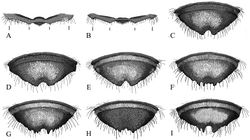
Female. Body length 11–12 mm. Mandible 4-toothed, with surface between teeth 3 and 4 angulate (Figure 4B). T2-3 with deep transverse basal grooves, T4 with shallow groove. T1-5 with apical fringes of white hair that covers marginal zone, T1-2 with thin fringes of white hair. T1-2 with white discal pubescence, T3-5 with black discal pubescence. T6 very slightly concave in profile and laterally in dorsal view; with black appressed pubescence and black erect setae basally. (Figure 5C). S1-5 with ivory setae; S6 with black setae.
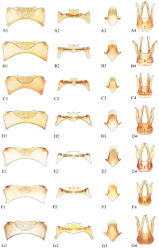
Male. Body length 9–11 mm.Mandible 3-toothed.Ocellocular distance less than ocelloccipital distance (Figure 4C). Head with white pubescence; vertex with black pubescence. Mesosoma with white pubescence, scutum with black pubescence. T2 with thin apical fringe of white hair (Figure 6J). T5 without complete apical fringe of white hair that covers marginal zone, may have some hair laterally. T6 with tomentum; punctures crowded, nearly contiguous (Figure 6C); transverse carina with distinct medial notch; true apical margin with submedial teeth closer to each other than lateral teeth, or distances equal (Figure 6A). Genitalia and hidden sterna shown in Figures 7C1–C4.
Variability
As with other Litomegachile species, individuals that appear early in the flight season may have pubescence that appears yellow instead of white.
Distribution of material examined:
USA: Arizona: Cochise, Pima and Santa Cruz Counties (Apr-Sep); California: Contra Costa, Mariposa Mendocino, Tuolumne and Yolo Counties (Jun.-Sep.); Utah: Washington County (May); Texas: Brewster County (May). MEXICO: Chihuahua and Sonora (Sep.); 103 females, 188 males.
Ecology
Megachile gentilis will nest in trap nests. Krombein (1967)[1] recovered nests from trap nests placed under live or dead mesquite branches in open desert. Parasites reared by Krombein (1967)[1] from these traps included Tetrastichus megachilidis Burks (Eulophidae), Trichodes horni Wolcott & Chapin (Cleridae), Anthrax atriplex Marston (Bombyliidae), and Anthrax irroratus Say(Bombyliidae).
Flower records
Clarkia biloba (Onagraceae), Eriodictyon sp. (Boraginaceae), Gaillardia pulchella (Asteraceae), Melilotus alba (Fabaceae), Parkinsonia sp. (Fabaceae), Polygonum aubertii (Polygonaceae).
Comments
Megachile gentilis is a western North American species, though records occur from eastern Texas, and populations are established in Hawaii (Snelling 2003[2]) (Figure 10).
Taxon Treatment
- Bzdyk, E; 2012: A revision of the Megachile subgenus Litomegachile Mitchell with an illustrated key and description of a new species (Hymenoptera, Megachilidae, Megachilini) ZooKeys, 221: 31-61. doi
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Krombein K (1967) Trap-nesting wasps and bees: life histories, nests and associates. Smithsonian Press, Washington DC, 570 pp.doi: 10.5962/bhl.title.46295
- ↑ Snelling R (2003) Bees of the Hawaiian Islands, Exclusive of Hylaeus (Nesoprosopis) (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society 76: 342-356
Images
|