| Notice: |
This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly.
This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Lackner T, Leschen R (2017) A monograph of the Australopacific Saprininae (Coleoptera, Histeridae). ZooKeys (689) : 1–263, doi. Versioned wiki page: 2017-08-14, version 161064, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Hypocaccus&oldid=161064 , contributors (alphabetical order): Pensoft Publishers.
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX:
@article{Lackner2017ZooKeys,
author = {Lackner, Tomáš AND Leschen, Richard A.B.},
journal = {ZooKeys},
publisher = {Pensoft Publishers},
title = {A monograph of the Australopacific Saprininae (Coleoptera, Histeridae)},
year = {2017},
volume = {},
issue = {689},
pages = {1--263},
doi = {10.3897/zookeys.689.12021},
url = {https://zookeys.pensoft.net/articles.php?id=12021},
note = {Versioned wiki page: 2017-08-14, version 161064, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Hypocaccus&oldid=161064 , contributors (alphabetical order): Pensoft Publishers.}
}
RIS/ Endnote:
Wikipedia/ Citizendium:
See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Taxonavigation
Ordo: Coleoptera
Familia: Histeridae
Name
Hypocaccus C. Thomson, 1867 – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of this genus is based on the taxa that occur in the Australopacific Region. Small to moderately sized, often metallic beetles; frontal stria usually well developed, straight; frons coarsely punctate or with several to multiple short to long transverse rugae. Pronotal disc either smooth (subgenus Baeckmanniolus Reichardt, 1926) or adorned with longitudinal rugae or very coarse punctures (subgenera Hypocaccus s.str. or Nessus Reichardt, 1932). Pronotum devoid of pronotal depressions, hypomeron asetose; both sets of prosternal striae present, carinal prosternal striae approximate, usually united apically posterad united lateral prosternal striae; prosternal foveae present, often well developed. Protibia on outer margin with 5–11 teeth topped by denticle; metatibia on outer margin with two (Hypocaccus s.str., Nessus) or three (subgenus Baeckmanniolus) rows of denticles.
Biology
Species of the subgenus Hypocaccus are found on the sandy shores of seas, lakes and rivers (sometimes also on inland sand dunes without the presence of water) where they prey upon dipteran larvae developing in various decomposing organic substances such as excrement, carcasses, seaweed, etc. Species of the subgenus Baeckmanniolus are confined to seashores with similar feeding habits (Lackner 2010[2]).
Distribution
With four recorded species (one of them introduced), the genus Hypocaccus is poorly represented in the Australopacific Region and has been collected in Australia, New Caledonia and New Guinea (Figs 753, 755, 756, 760). We would expect the widespread species H. (H.) brasiliensis (see Mazur 2011[3]) or H. (H.) sinae to be eventually collected elsewhere within the Region.
Species of the genus Hypocaccus are typified by the presence of smooth to rugose frons, which can be also furnished with transverse rugae and cannot be confused with any other Australian Saprininae.
Key to the subgenera of the genus Hypocaccus of the Australopacific Region
Taxon Treatment
- Lackner, T; Leschen, R; 2017: A monograph of the Australopacific Saprininae (Coleoptera, Histeridae) ZooKeys, (689): 1-263. doi
Images
| Figures 129–134. 129 Hypocaccus (Nessus) interpunctatus interpunctatus (Schmidt, 1885) head, dorsal view 130 antennal club, dorsal view 131 prosternum 132 mesoventrite 133 lateral disc of metaventrite + metepisternum, with visible mesotibia 134 metatibia, dorsal view. |
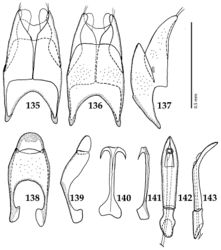
| Figures 135–143. 135 Hypocaccus (Nessus) interpunctatus interpunctatus (Schmidt, 1885) male terminalia: 8th sternite + 8th tergite, ventral view 136 ditto, dorsal view 137 ditto, lateral view 138 male terminalia: 9th + 10th tergites, dorsal view 139 ditto, lateral view 140 male terminalia: spiculum gastrale, ventral view 141 ditto, lateral view 142 male terminalia: aedeagus, dorsal view 143 ditto, lateral view. |
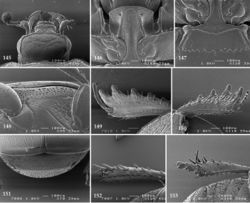
| Figures 145–153. 145 Hypocaccus (Hypocaccus) brasiliensis (Paykull, 1811) head, dorsal view 146 prosternum 147 mesoventrite 148 lateral disc of metaventrite + metepisternum 149 protibia, dorsal view 150 ditto, ventral view 151 propygidium + pygidium 152 metatibia, dorsal view 153 ditto, ventral view. |
| Figures 154–160. 154 Hypocaccus (Hypocaccus) brasiliensis (Paykull, 1811) male terminalia: 8th sternite + 8th tergite, ventral view 155 ditto, dorsal view 156 ditto, lateral view 157 male terminalia: 9th + 10th tergites, dorsal view; spiculum gastrale, ventral view 158 male terminalia: 9th + 10th tergites; spiculum gastrale, lateral view 159 male terminalia: aedeagus, dorsal view 160 ditto, lateral view. |
| Figures 162–173. 162 Hypocaccus (Hypocaccus) sinae (Marseul, 1862) head, dorsal view 163 antennal club, dorsal view 164 ditto, ventral view 165 mentum, ventral view 166 propygidium + pygidium 167 prosternum 168 mesoventrite 169 lateral disc of metaventrite + metepisternum 170 protibia, dorsal view 171 ditto, ventral view 172 mesotibia, ventral view 173 metatibia, ventral view. |
| Figures 174–182. 174 Hypocaccus (Hypocaccus) sinae (Marseul, 1862) male terminalia: 8th sternite + 8th tergite, ventral view 175 ditto, dorsal view 176 ditto, lateral view 177 male terminalia: 9th + 10th tergites, dorsal view 178 ditto, lateral view 179 male terminalia: spiculum gastrale, ventral view 180 ditto, lateral view 181 male terminalia: aedeagus, dorsal view 182 ditto, lateral view. |
| Figures 184–192. 184 Hypocaccus (Baeckmanniolus) varians varians (Schmidt, 1890) head, dorsal view 185 antennal club, ventral view 186 mentum, ventral view 187 propygidium + pygidium 188 prosternum 189 mesoventrite 190 lateral disc of metaventrite + metepisternum 191 protibia, dorsal view 192 ditto, ventral view. |
| Figures 193–201. 193 Hypocaccus (Baeckmanniolus) varians varians (Schmidt, 1890) male terminalia: 8th sternite + 8th tergite, ventral view 194 ditto, dorsal view 195 ditto, lateral view 196 male terminalia: 9th + 10th tergites, dorsal view 197 ditto, lateral view 198 male terminalia: spiculum gastrale, ventral view 199 ditto, lateral view 200 male terminalia: aedeagus, dorsal view 201 ditto, lateral view. |
|
Other References
- ↑ Lewis G (1899) On a New Species of Histeridae and Notices of Others. Annals and Magazine of Natural History Series 7, 4: 1–29.
- ↑ Lackner T (2010) Review of the Palaearctic genera of Saprininae (Coleoptera: Histeridae). Acta Entomologica Musei Nationalis Pragae, 50 (Supplementum): 1–254.
- ↑ Mazur S (2011) A concise catalogue of the Histeridae (Coleoptera). Warsaw University of Life Sciences, SGGW Press, Warsaw 332 pp.