Hedychridium
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Paukkunen2015ZooKeys, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Paukkunen2015ZooKeys">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Hymenoptera
Familia: Chrysididae
Name
Hedychridium Abeille de Perrin, 1878 – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Hedychridium Abeille de Perrin, 1878: 3.
- Euchrum Semenov, 1954: 103.
Note
This genus comprises a heterogeneous group of small colourful species ranging from 2 to 7 mm in length. Characteristic morphological features include the single perpendicular tooth of the tarsal claw and the transverse pronotal carina (Kimsey and Bohart 1991[1]). The posterior margin of T3 is evenly rounded, without any angular projections. The biology of most species is poorly known, but according to published records, the larvae develop as nest parasites of ground-nesting crabronid wasps and solitary bees. Hedychridium is the second largest genus of Chrysididae and includes more than 300 recognised species worldwide. The highest diversity is found in arid parts of the Holarctic Region and southern Africa. A total of 86 species are known from Europe (Rosa and Soon 2012[2]). Of these, seven occur in the Nordic and Baltic countries (Paukkunen et al. 2014[3]). The genus is here divided into three species-groups according to Linsenmaier (1968[4], 1997[5]).
Key to Hedychridium species of the Nordic and Baltic countries
Taxon Treatment
- Paukkunen, J; Berg, A; Soon, V; Ødegaard, F; Rosa, P; 2015: An illustrated key to the cuckoo wasps (Hymenoptera, Chrysididae) of the Nordic and Baltic countries, with description of a new species ZooKeys, (548): 1-116. doi
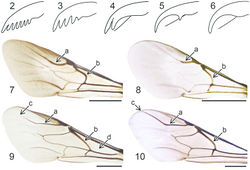
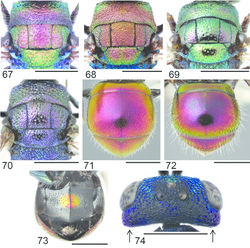
Images
|
Other References
- ↑ Kimsey L, Bohart R (1991) [1990] The Chrysidid Wasps of the World. Oxford Press, New York, 652 pp.
- ↑ Rosa P, Soon V (2012) Fauna Europaea: Chrysididae. In: Mitroiu M (Ed.) Fauna Europaea: Hymenoptera, version 2.5. http://www.faunaeur.org [accessed 1 April 2015]
- ↑ Paukkunen J, Rosa P, Soon V, Johansson N, Ødegaard F (2014) Faunistic review of the cuckoo wasps of Fennoscandia, Denmark and the Baltic countries (Hymenoptera: Chrysididae). Zootaxa 3864: 1–67. doi: 10.11646/zootaxa.3864.1.1
- ↑ Linsenmaier W (1968) Revision der Familie Chrysididae (Hymenoptera), Zweiter Nachtrag. Mitteilungen der Schweizerischen Entomologischen Gesellschaft 41: 1–144.
- ↑ Linsenmaier W (1997) Die Goldwespen der Schweiz. Veröffentlichungen aus dem Natur-Museum Luzern 9: 1–139.