Fortuynia smiti
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Ermilov2013ZooKeys318, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Ermilov2013ZooKeys318">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Sarcoptiformes
Familia: Fortuyniidae
Genus: Fortuynia
Name
Fortuynia smiti Ermilov, Tolstikov, Mary & Schatz sp. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Diagnosis
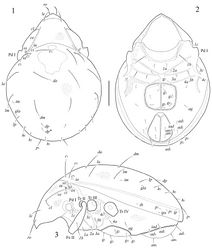
Body size 564–614 × 381–431. Body surface microfoveolate. Lamellar lines, internal and lateral ridges developed. Rostral setae weakly thickened, with short cilia; lamellar setae thin, slightly barbed. Interlamellar and exobothridial setae minute. Sensilli short, clavate, smooth. Notogaster with 14 pairs of setae and one pair of setal alveoli (c3). Length of setae c1, da > c2, dm, la, lm > p1 > lp, h3 > dp, h1, h2 > p1, p2. Adanal setae ad1 longer than other adanal setae.
Description
Male. Measurements. Body length 581 (holotype, male), 564–614 (six paratypes, all males); body width 398 (holotype), 381–431 (six paratypes, all males).
Integument. Body color brown to yellow-brownish. Body surface microfoveolate (clearly visible under high magnification, ×1000). Lateral podosomal regions with tuberculate cerotegument (diameter of tubercles up to 6).
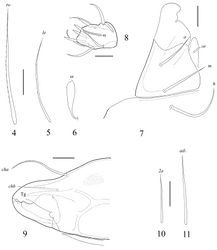
Prodorsum. Rostrum rounded. Lamellar lines (ce) strong, equal to half of prodorsum. Internal ridges (ci) present, very thin, reaching insertions of interlamellar setae. Anterior part of lamellar lines with short lateral ridges (cl), which are located perpendicularly to them. Rostral setae (ro, 69–82) setiform, weakly thickened, with short cilia, set on small tubercles. Lamellar setae (le, 41–45) setiform, thin, slightly barbed. Interlamellar (in) and exobothridial (ex) setae minute (1), poorly visible. Sensilli (ss, 32–36) curved backwards, with short stalk and longer clavate, smooth head.
Notogaster. Lenticulus present, with amorphic borders. Notogastral region with 14 pairs of setiform, smooth notogastral setae and one pair of setal alveoli (c3). Setae c1, da (90–102) longer than c2, dm, la, lm (69–82), p1 (30–36), lp, h3 (28–32), dp, h1, h2 (20–24); p1, p2 shortest (4–6). Lyrifissures ia, im, ip, ih and ips and opisthonotal gland openings (gla) distinct, located typically for the genus.
Gnathosoma. Subcapitulum longer than wide (118–205 × 143–151). Subcapitular setae setiform, smooth; h (82–86) longer than a and m (both 53–57). Lips only with one spiniform seta (or, 10–12). Palps (123–131) with setation 0–2–1–3–9(+ω). All setae smooth. Solenidion weakly thickened, blunt-ended, pressed to surface of tarsus, not attached with eupathidium. Chelicerae (188–205) with two barbed setae; cha (69–73) longer than chb (45–49). Trägårdh’s organ (Tg) long, conical.
Epimeral and lateral podosomal regions. Apodemes 1, 2, 3 and sejugal well developed. Apodemes 2 and sejugal fused medially. Epimeral setal formula 3–1–3–2; setae setiform, smooth. Setae 1b (49–61) longer than 3b (41–49), 1a, 2a, 3a, 3c, 4a, 4c (24–36); 1c shortest (16–20). Pedotecta I (Pd I) of medium size, concave.
Anogenital region. Anogenital setae setiform, thin, smooth. Five pairs of genital (g1–g5), one pair of aggenital (ag), two pairs of anal (an1, an2) and the anterior two pairs of adanal (ad2, ad3) setae similar in length (28–32); only the first pair of adanal setae ad1 longer (41–53). Lyrifissures iad located in paraanal position.
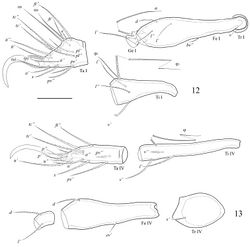
Legs. Claw of each leg large, smooth. Porose areas developed typically for the genus (Bayartogtokh et al. (2009)[1]. Formulae of leg setation and solenidia: I (1–4–2–3–18) [1–2–2], II (1–4–2–3–15) [1–1–2], III (2–3–1–3–15) [1–1–0], IV (1–2–2–3–12) [0–1–0]; homology of setae and solenidia indicated in Table 2. Setae setiform, well or slightly barbed except smooth p on tarsi I, II and s. Famulus (e) short, straight, weakly blunt-ended. All solenidia long setiform, pointed.
| Leg | Trochanter | Femur | Genu | Tibia | Tarsus |
| I | v’ | d, (l), bv’’ | (l), σ | (l), v’, φ1, φ2 | (ft), (tc), (it), (p), (u), (a), s, (pv), (pl), e, ω1, ω2 |
| II | v’ | d, (l), bv’’ | (l), σ | (l), v’, φ | (ft), (tc), (it), (p), (u), (a), s, (pv), ω1, ω2 |
| III | l’, v’ | d, l’, ev’ | l’, σ | l’, (v), φ | (ft), (tc), (it), (p), (u), (a), s, (pv) |
| IV | v’ | d, ev’ | d, l’ | l’, (v), φ | ft’’, (tc), (p), (u), (a), s, (pv) |
Material examined
Holotype (male) and six paratypes (all males): Locality 02.
Type deposition
The holotype (in alcohol) is deposited in the collection of the Zoological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, St. Petersburg, Russia; two paratypes (in alcohol) are deposited in the collection of the Siberian Zoological Museum, Novosibirsk, Russia; four paratypes (in alcohol) are deposited in the collection of the Tyumen State University Museum of Zoology, Tyumen, Russia.
Etymology. The species is named after our colleague, the renowned acarologist, Dr. Harry Smit (Netherlands Centre for Biodiversity Naturalis, Leiden, The Netherlands), who has collected the specimens of Fortuynia smiti sp. n.
Comparison
Fortuynia smiti sp. n. is most similar to Fortuynia marina Hammen, 1960 from New Guinea (Hammen 1960[2]) in having following combination of morphological characters: body of medium size; presence of lamellar lines and internal ridges; presence of alveoli notogastral setae c3. However it differs from the latter by the long notogastral setae dm, lm, c2, p1, epimeral setae 3b and adanal setae ad1 (versus short in Fortuynia marina) and the presence of prodorsal lateral ridges (versus absent in Fortuynia marina).
Original Description
- Ermilov, S; Tolstikov, A; Mary, N; Schatz, H; 2013: Oribatid mites (Acari, Oribatida) from riverine environments of some islands in Oceania ZooKeys, 318: 47-57. doi
Other References
- ↑ Bayartogtokh B, Chatterjee T, Chan B, Ingole B (2009) New species of marine littoral mites (Acari: Oribatida) from Taiwan and India, with a key to the World’s species of Fortuynia and notes on their distributions. Zool. Stud. 48 (2): 243-261.
- ↑ Hammen L (1960) Fortuynia marina nov. gen., nov. spec., an oribatid mite from the intertidial zone in Netherlands New Guinea. Zool. Med. 37 (1): 1-9.
Images
|