| Notice: |
This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly.
This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Sun N, Marusik Y, Tu L (2014) Acanoides gen. n., a new spider genus from China with a note on the taxonomic status of Acanthoneta Eskov & Marusik, 1992 (Araneae, Linyphiidae, Micronetinae). ZooKeys 375 : 75–99, doi. Versioned wiki page: 2014-01-30, version 41278, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Acanoides_beijingensis&oldid=41278 , contributors (alphabetical order): Pensoft Publishers.
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX:
@article{Sun2014ZooKeys375,
author = {Sun, Ning AND Marusik, Yuri M. AND Tu, Lihong},
journal = {ZooKeys},
publisher = {Pensoft Publishers},
title = {Acanoides gen. n., a new spider genus from China with a note on the taxonomic status of Acanthoneta Eskov & Marusik, 1992 (Araneae, Linyphiidae, Micronetinae)},
year = {2014},
volume = {375},
issue = {},
pages = {75--99},
doi = {10.3897/zookeys.375.6116},
url = {http://www.pensoft.net/journals/zookeys/article/6116/abstract},
note = {Versioned wiki page: 2014-01-30, version 41278, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Acanoides_beijingensis&oldid=41278 , contributors (alphabetical order): Pensoft Publishers.}
}
RIS/ Endnote:
Wikipedia/ Citizendium:
See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Taxonavigation
Ordo: Araneae
Familia: Linyphiidae
Genus: Acanoides
Name
Acanoides beijingensis Sun & Marusik & Tu, 2014 sp. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Type-locality
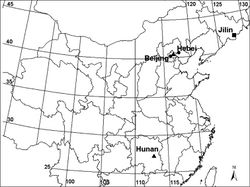
China, Beijing: Mt. Yangtaishan, 39°20.15'N, 115°34.52'E, alt. ca 320m, 15 Oct. 2007, L. Tu leg.
Type-specimens
Holotype, ♂ (CNU), China, Beijing, Mt. Yangtaishan, 39°20.15'N, 115°34.52'E, alt. ca 320 m, 15 Oct. 2007, L. Tu leg. Paratypes, 2 ♂♂ and 3 ♀♀ (CNU), same data as holotype.
Additional material examined
1 ♂ and 2 ♀♀ (CNU), China, Hebei Province, Mt. Wulingshan, 40°33.61'N, 117°29.69'E, alt. ca 1100 m, 12 Aug. 2009, L. Tu leg.
Diagnosis
The male of Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. can be distinguished from Acanoides hengshanensis by the spine-shaped lamella characteristica (Figs 2D, 4C), ribbon-like in the latter (Figs 3D, 5C); by the hook-shaped terminal apophysis (Fig. 4C), straight in the latter (Fig. 5D); and by the presence of a distal suprategular apophysis (Fig. 4A), absent in the latter. The female is distinct by having the epigynum two times longer than wide (Fig. 2F), shorter than wide in Acanoides hengshanensis (Fig. 3F); and by the presence of a remnant epigynal cavity (Fig. 2G), totally absent in Acanoides hengshanensis (Fig. 3G).
Description
Male holotype (Fig. 1A, C): Total length 2.69. Carapace 1.22 long, 1.01 wide. Abdomen 1.39 long, 0.88 wide. Lengths of legs: I 3.88 (1.05 + 1.18 + 0.99 + 0.66); II 3.02 (1.03 + 0.73 + 0.69 + 0.57); III 2.66 (0.87 + 0.88 + 0.51 + 0.40); IV 3.78 (1.12 + 1.09 + 0.93 + 0.64). Female (Fig. 1B): Total length 2.12. Carapace 0.93 long, 0.78 wide. Abdomen 1.25 long, 0.83 wide. Lengths of legs: I 6.10 (1.68 + 2.04 + 1.43 + 0.95); II 5.43 (1.56 + 1.74 + 1.24 + 0.89); III 4.39 (1.24 + 1.13 + 1.10 + 0.75); IV 5.88 (1.79 + 1.78 + 1.46 + 0.83). Tm I: 0.20. For other somatic features see description of the genus.
Male palp (Figs 2A–C, 4A–B). Cymbium with proximal apophysis. Paracymbium narrow, half rounded lateral tooth strongly sclerotized. Distal suprategular apophysis blunt, not modified as pit hook. Embolic division: radix long and narrow; Fickert’s gland located in the membranous area connecting radix and embolus; embolus main body short and wide, strongly sclerotized, with serrated area on ventral surface; embolus proper sharp with pointed thumb and tail-like apex at each side; unbranched lamella characteristica long and slender, with sharp and strongly sclerotized apex; terminal apophysis hook-shaped with distal membrane.
Epigynum (Figs 2F–H, 4G–H). Two times longer than wide, wrinkled basal part extensible and ventrally folded in constricted state. Median plate and epigynal cavity present, without scape and stretcher. Copulatory openings opened dorsally.
Etymology
The species name refers to the type locality.
Variation
Males (n = 3). Total length 2.61–2.73. Carapace: 1.13–1.27 long, 0.95–1.05 wide. Abdomen 1.34–1.45 long, 0.71–0.99 wide.
Females (n = 3). Total length 2.10–2.23. Carapace: 0.90–0.96 long, 0.74–0.78 wide. Abdomen: 1.10–1.38 long, 0.79–0.88 wide.
Distribution
China (Beijing, Hebei) (Fig. 7).
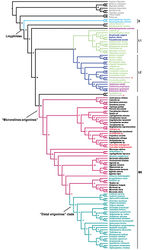
Although Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. looks quite different from Acanoides hengshanensis in the shape of the male paracymbium and in terms of female epigynal morphology, the strongly sclerotized embolus main body and the sharp embolus proper, the location of Fickert’s gland, the presence of a ventrally folded extensive area of the epigynal basal part and the absence of a scape and stretcher, shared by the two species suggest they are closely related. A close relationship between the two species is additionally supported by the phylogenetic analysis (Appendix - Fig. S1).
Original Description
- Sun, N; Marusik, Y; Tu, L; 2014: Acanoides gen. n., a new spider genus from China with a note on the taxonomic status of Acanthoneta Eskov & Marusik, 1992 (Araneae, Linyphiidae, Micronetinae) ZooKeys, 375: 75-99. doi
Images
| Figure 1. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. ( A–C) and Acanoides hengshanensis ( D–F). A male, dorsal B female, dorsal C male, lateral, rectangle indicates ventrolateral rows of bristles on Mt I D male, lateral, rectangle indicates ventrolateral rows of bristles on Mt I E male, dorsal F female, dorsal. [Scale bars: mm]. |
| Figure 2. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. A male palp, prolateral B male palp, prolateral, with embolic division removed C male palp, retrolateral D embolic division, ventral E embolic division, dorsal F epigynum, ventral G epigynum, dorsal H epigynum, lateral. CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DP dorsal plate; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; FiG Fickert’s gland; LC lamella characteristica; MP median plate; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermathecae; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm]. |
| Figure 3. Acanoides hengshanensis. A male palp, prolateral B male palp, ventral C male palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates pointed tooth on posterolateral margin D embolic division, ventral E embolic division, dorsal F epigynum, ventral G epigynum, dorsal. CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DP dorsal plate; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; FiG Fickert’s gland; LC lamella characteristica; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm]. |
| Figure 4. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. A palp (embolic division removed), prolateral B palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates half rounded lateral tooth on paracymbium C embolic division, ventral D embolic division, dorsal E detail of D F detail of C G epigynum, ventral H epigynum, dorsal. AX apex of embolus; CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DM distal membrane of terminal apophysis; DSA distal suprategular apophysis; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; LC lamella characteristica; MP median plate; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; SE serrated area on embolus; SPT suprategulum; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm]. |
| Figure 5. Acanoides hengshanensis. A palp (embolic division removed), prolateral B palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates pointed tooth on posterolateral margin C embolic division, ventral D embolic division, dorsal E detail of D F detail of C G epigynum, ventral H epigynum, dorsal. AX apex of embolus; CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DM distal membrane of terminal apophysis; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; LC lamella characteristica; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; SPT suprategulum; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm]. |
| Figure S1. Linyphiid phylogeny resulting from Maximum Likelihood analysis based on molecular data. Numbers at the nodes are bootstrap value. Branches in color indicate the four robustly supported clades within linyphiids: S Stemonyphantes clade (blue) L1 “linyphiines”-1 clade (pale green) L2 “linyphiines-2” clade (dark blue) ME “micronetines-erigonines” clade (red, with “Distal erigonines” clade in green). Taxa in different colors sampled from different groups: grey, outgroup; blue, Stemonyphantinae; pale green, Linyphiinae; dark blue, Mynogleninae; pink, Dubiaraneinae; black, Micronetinae; red, Ipainae, Acanthoneta and Acanoides gen. n.; green, Erigoninae. Red stars indicate the two out-group taxa: cyatholipid Alaranea and theridiosomatid Theridiosoma embedded within Linyphiidae. |
|
![Figure 1. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. (A–C) and Acanoides hengshanensis (D–F). A male, dorsal B female, dorsal C male, lateral, rectangle indicates ventrolateral rows of bristles on Mt I D male, lateral, rectangle indicates ventrolateral rows of bristles on Mt I E male, dorsal F female, dorsal. [Scale bars: mm].](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=ZooKeys-375-075-g001.jpg&width=248)
![Figure 2. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. A male palp, prolateral B male palp, prolateral, with embolic division removed C male palp, retrolateral D embolic division, ventral E embolic division, dorsal F epigynum, ventral G epigynum, dorsal H epigynum, lateral. CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DP dorsal plate; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; FiG Fickert’s gland; LC lamella characteristica; MP median plate; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermathecae; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm].](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=ZooKeys-375-075-g002.jpg&width=187)
![Figure 3. Acanoides hengshanensis. A male palp, prolateral B male palp, ventral C male palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates pointed tooth on posterolateral margin D embolic division, ventral E embolic division, dorsal F epigynum, ventral G epigynum, dorsal. CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DP dorsal plate; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; FiG Fickert’s gland; LC lamella characteristica; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm].](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=ZooKeys-375-075-g003.jpg&width=213)
![Figure 4. Acanoides beijingensis sp. n. A palp (embolic division removed), prolateral B palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates half rounded lateral tooth on paracymbium C embolic division, ventral D embolic division, dorsal E detail of D F detail of C G epigynum, ventral H epigynum, dorsal. AX apex of embolus; CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DM distal membrane of terminal apophysis; DSA distal suprategular apophysis; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; LC lamella characteristica; MP median plate; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; SE serrated area on embolus; SPT suprategulum; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm].](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=ZooKeys-375-075-g004.jpg&width=189)
![Figure 5. Acanoides hengshanensis. A palp (embolic division removed), prolateral B palp, retrolateral, arrow indicates pointed tooth on posterolateral margin C embolic division, ventral D embolic division, dorsal E detail of D F detail of C G epigynum, ventral H epigynum, dorsal. AX apex of embolus; CG copulatory groove; CO copulatory opening; DM distal membrane of terminal apophysis; EA extensible area of epigynal basal part; EM embolic membrane; EP embolus proper; FG fertilization groove; LC lamella characteristica; P paracymbium; PCA proximal cymbial apophysis; R radix; S spermatheca; SPT suprategulum; TA terminal apophysis; TH thumb of embolus; VP ventral plate. [Scale bars: mm].](https://species-id.net/o/thumb.php?f=ZooKeys-375-075-g005.jpg&width=188)