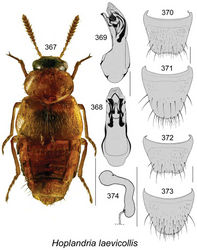
Hoplandria laevicollis
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Webster2016ZooKeys, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Webster2016ZooKeys">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Coleoptera
Familia: Staphylinidae
Genus: Hoplandria
Name
Hoplandria laevicollis (Notman, 1920) – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Material examined
New Brunswick, Northumberland Co., ca, 2.5 km W of Sevogle, 47.0876°N, 65.8613°W, 21.VIII.2013, 27.VIII.2013, R.P. Webster // Old Pinus banksiana forest, in rotten boletus mushrooms (8 ♀, RWC); ca. 1.5 km NW of Sevogle, 47.0939°N, 65.8387°W, 6–21.VIII.2013, C. Alderson & V. Webster // Populus tremuloides stand with a few conifers, Lindgren funnel trap 1 m high under Populus tremuloides (1 ♀, RWC).
Natural history
Most adults of Hoplandria laevicollis from NB were found in rotten bolete mushrooms in an old jack pine forest. One individual was captured in a Lindgren funnel trap in a stand of trembling aspen. Adults were collected during August.
Distribution in Canada and Alaska
ON, QC, NB (Génier 1989[1]; Brunke et al. 2012[2]; Bousquet et al. 2013[3]).
Comments
All specimens of Hoplandria laevicollis from NB were females. The identification was based on the description and key in Génier (1989)[1]. It should be noted that female characters are not as diagnostic as those of males, and thus the determination of these specimens should be considered as provisional until males are obtained from the sites where the species was found.
Taxon Treatment
- Webster, R; Klimaszewski, J; Bourdon, C; Sweeney, J; Hughes, C; Labrecque, M; 2016: Further contributions to the Aleocharinae (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae) fauna of New Brunswick and Canada including descriptions of 27 new species ZooKeys, (573): 85-216. doi
Images
|
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Génier F (1989) A revision of the genus Hoplandria Kraatz of America north of Mexico (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae, Aleocharinae). Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada No. 150: 3–59.
- ↑ Brunke A, Klimaszewski J, Dorval J, Bourdon C, Paiero S, Marshall S (2012) New species and distributional records of Aleocharinae (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae) from Ontario, Canada, with a checklist of recorded species. ZooKeys 186: 119–206. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.186.2947
- ↑ Bousquet Y, Bouchard P, Davies A, Sikes D (2013) Checklist of beetles (Coleoptera) of Canada and Alaska. Pensoft Series Faunistica No. 109, Sofia-Moscow, 402 pp.