Cryptophyton jedsmithi
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Williams2013ZooKeys283, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Williams2013ZooKeys283">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Genus: Cryptophyton
Name
Cryptophyton jedsmithi Williams, 2013 sp. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Species diagnosis
Stolons ribbon-like to somewhat broadened in some areas. Anthosteles hemispherical, arise directly from basal stolons, elevated stolonic bars or transverse platforms absent. Anthocodial armature absent. Sclerites of stolons and anthosteles 0.06–0.10 mm in diameter, mostly spiny balls or stellate bodies with projecting processes in three dimensions.
Type material
Holotype. CAS 177194. North America, U.S.A., California, San Diego County, San Diego, Point Loma, 32°42'N, 117°15'20"W, 12 February 2006, collector: Jeff Goddard, one specimen wet-preserved in 95% ethanol.
Habitat and distribution
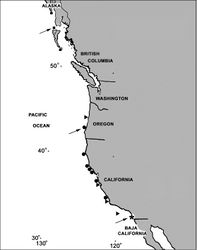
(Figure 19): Under a boulder in the low rocky intertidal zone at the type locality.
Etymology
The species is named for Jedediah Strong Smith, American trailblazer and cartographer, who explored vast regions of western North America between 1822 and 1831, and along the Pacific Coast, including San Diego in December of 1826 (Brooks 1977[1]) – the area of the type locality of the new species.
Description
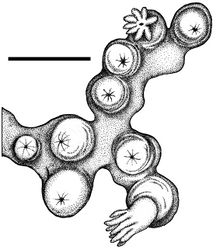
Colonial morphology (Figures 1A, 2). The holotype consists of approximately eighty-five polyps arising from flattened basal stolons. The stolons encrust a piece of dead cheilostomatid bryozoan, 32 mm long by 20 mm wide. The surface of the bryozoan is interspersed with several calcareous tubes of a serpulid polychaete.
Polyps (Figures 1B–C). Anthosteles are moundlike, rounded, hemispherical to subcylindrical. Anthocodiae are mostly retracted within the anthosteles, although a few are emergent. The anthosteles are approximately equal in height and diameter, mostly 1–1.4 mm.
Sclerites (Figures 1D–E, 3, 4). Sclerites of the coenencyme and anthosteles resemble spiny balls or stellate bodies with projecting processes in three dimensions; 0.05 – 0.10 mm long. Sclerites are absent from the anthocodiae and polyp bodies.
Color (Figures 1A–C). Color in life: the anthosteles are pale orange and the anthocodiae are white. Wet-preserved holotype: stolons and anthosteles light grayish white, while the emergent anthocodiae are white.
Differential diagnosis
Two species of the genus Cryptophyton are known, Cryptophyton goddardi Williams, 2000 and Cryptophyton jedsmithi sp. n. The two species differ in sclerite shape. Those of Cryptophyton goddardi are irregularly-shaped radiates, tuberculated rods, and shuttles (Williams 2000[2]: 337), while those of Cryptophyton jedsmithi sp. n. mostly resemble spiny balls or stellate bodies (Figures 1D–E, 3–4).
The geographic range of Cryptophyton goddardi was originally known only from the type locality of central Oregon on the Pacific Coast of the United States, but has recently been extended southwards to southern California, and has been collected at seven locations (Figure 19), while Cryptophyton jedsmithi sp. n. is known only from the type locality – San Diego, California (Figure 19).
Key to the species of Cryptophyton
Original Description
- Williams, G; 2013: New taxa and revisionary systematics of alcyonacean octocorals from the Pacific coast of North America (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) ZooKeys, 283: 15-42. doi
Other References
- ↑ Brooks G (editor) (1977) The southwest expedition of Jedediah S. Smith, his personal account of the journey to California, 1826–1827. Western Frontiersman Series 18. The Arthur H. Clark Company, Glendale, California, 259 pp.
- ↑ Williams G (2000) A new genus and species of stoloniferous octocoral (Anthozoa: Clavulariidae) from the Pacific coast of North America. Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden 73: 333–343.
Images
|