Calisto bradleyi
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Aguila2012ZooKeys165, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Aguila2012ZooKeys165">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Lepidoptera
Familia: Nymphalidae
Genus: Calisto
Name
Calisto bradleyi Munroe, 1950 comb. n. – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Calisto smintheus bradleyi Munroe 1950[1]: 227, Torre 1952[2]: 63, Torre 1954[3]: 121, Torre 1968[4]: 7
- Calisto sibylla bradleyi Brown and Heineman 1972[5]: 51, Alayo and Hernández 1987[6]: 41, Fontenla and Rodríguez 1990[7]: 9, Smith et al. 1994[8]: 57, Lamas 2004[9]: 207
Diagnosis
Calisto bradleyi resembles Calisto muripetens and Calisto occulta more than its other congeners. It can be separated from these species by the presence of an apical lobe at the androconial patch, and by having an iridescent blue band edging the black dot of the anal lobe at the UNHW. Other differences were treated in the Diagnosis section of those species. From other Cuban (except Calisto bruneri), Hispaniolan and Bahamian species differs by the same characters and by have fewer white dots at UNHW. Its female genitalia is also diagnostic due to its proportionally smaller size and its thinner dorsal crown. The Hispaniolan Calisto confusa, Calisto hysius, Calisto obscura, and Calisto pauli are superficially similar but are smaller,and have four white dots at the UNHW.
Description
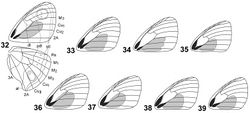
FWL: 17–20 mm ♂, 20–21 mm ♀. UPFW outer third and area anterior to apical half of androconial patch pale grayish brown, basal area anterior to patch darker (Figs 19, 20); costal two thirds and androconial patch dark brown, almost black. UPHW uniform dark brown, slightly paler than androconial. Androconial patch distinct from surrounding areas, approximately triangular with a rounded lobe at apex, not entering into cell, about one half the length of FW (Fig. 38). Lines at UN of wings with little if any pale shade of external side (Figs 21, 30). UNHW background pale brown heavily mixed with ochre scaling basal to pdl. Post discal area on UNHW with three white dots at M1– M2, M2–M3, M3–Cu1, with that on M2–M3 larger, smaller dots can gone in rubbed specimens. UNHW lobe with a black dot anteriorly edged by a small band of iridescent blue scales. Male genitalia with tegumen about half the length of uncus, tapering gradually toward apex and arched along its length (Fig. 46); uncus strongly arched; digitiform projection of valvae stout, slightly arched toward venter; aedeagus with two sinuations of left side at apical half, the basal one smaller. Female genitalia small (Fig. 54); dorsal crown of sterigmal ring very narrow; corpus bursae small and broad, about two fifths the length of ductus bursae; ductus bursae very thin.
T
ype material
Holotype♂: Pinar del Río, Sierra de Rangel (currently Sierra del Rosario), Río Tacoluco (almost surely Río Taco Taco), 3 March 1939, J. C. Bradley. Location unknown, not examined.
Additional material
14 ♂, 13 ♀. Pinar del Río: Viñales 150 m, X/1985, J. L. Fontenla, genitalia ♂ & ♀ in glycerin, slides RNA202(legs & labial palpus)/260(wings) (1 ♂, 2 ♀); no collection data but probably the same same as for anterior, genitalia ♂ & ♀ in glycerin, slides RNA181 (androconial scales) /244/245/262/263/270/271 (wings)/247/ 265/278(legs & labial palpus) (6 ♂, 7 ♀); cuabales ladera sur de Cajálbana 150 m, 22°46'33.1"N, 83°26'22.1"W, III/2002, R. Núñez, DNA voucher PM15–08 (M054), genitalia in glycerin (1 ♀); Viñales, base norte mogote Dos Hermanas 140 m, 22°37'16.4"N, 83°44'40.3"W, 17/IV/2009, R. Núñez & E. Oliva, DNA vouchers PM07–24 (M043), PM07–25 (M044) & PM07–26 (M045) (6 ♂, 3 ♀). Artemisa: Pinar del Río (currently Artemisa), Sierra del Rosario, El Taburete 300 m, 22°50'11"N, 82°55'24"W, 9/X/2007, R. Núñez, DNA voucher PM07–06 (M006), genitalia in glycerin (1 ♂).
Distribution
Calisto bradleyi occurs in the major mountain range of western Cuba, Guaniguanico, from El Taburete, at Sierra del Rosario, 90 km west to Viñales valley, always at low elevations (Figs 56, 59). The species was previously known only from the type locality, Rangel, and Viñales (Munroe 1950[1]; Fontenla 1987b[10]). Attempts to find it at the type locality were made by Torre (1968)[4] and ourselves without success. Here we recorded it for the first time from Cajálbana and El Taburete widening its distribution to the eastern most portion of Guaniguanico mountain range.
Immature stages
Unknown.
Habitat and biology
The species inhabits various vegetation types throughout its distribution but can only be found in areas where original elements are still dominant. Habitats include the evergreen forest at El Taburete, the mogote vegetation complex at Viñales, and the dry scrub on serpentine soil at Cajálbana (Figs 64, 65). In Viñales valley, Pinar del Río, the species was flying in the shadow of the base of mogotes (limestone hills of almost vertivcal slopes) appearing occasionally in sunny places. There it was observed feeding on flowersof Stachyterpheta cayenensis, Hyptis verticilla, and Urena lobata, and a mating pair was observed at 3:30 pm in April 2009.
Remarks
The type specimen of Calisto smintheus bradleyi is apparently lost. Searching of the type specimen at the different collections mentioned by Munroe (1950)[1], CUIC, AMNH, MCZ, and CMNH, was fruitless. However, based on the examination of original description and since the other only species in its range of distribution, Calisto herophile, is rather different, it can be easily identified.
DNA analyses are somewhat ambiguous about the relationships of Calisto bradleyi. The mitochondrial dataset suggests that Calisto bradleyi is paraphyletic with regard to Calisto herophile and one individual of Calisto muripetens (Fig. 66), while the nuclear data place the monophyletic Calisto bradleyi in a clade with Calisto occulta and Calisto muripetens. The COI distance between the sister species Calisto herophile and Calisto bradleyi is 1.91%. Nonetheless, the status of species in both cases is still valid as the molecular phylogenies consistently separate the lineages (Fig. 66). Therefore, we prefer to treat them as separate entities, proposing the species status for Calisto bradleyi, potentially phylogenetically close to Calisto herophile.
Taxon Treatment
- Aguila, R; Plasencia, E; Maravi, P; Wahlberg, N; 2012: Cuban Calisto (Lepidoptera, Nymphalidae, Satyrinae), a review based on morphological and DNA data ZooKeys, 165: 57-105. doi
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Munroe E (1950) The systematics of Calisto (Lepidoptera, Satyrinae), with remarks on the evolutionary and zoogeographic significance of the genus. Journal of the New York Entomological Society 58 (4): 211-241.
- ↑ Torre S (1952) Datos taxonómicos sobre lepidópteros, con notas sobre algunas species cubanas, segunda parte. Memorias de la Sociedad Cubana de Historia Natural 21 (1): 61-70.
- ↑ Torre S (1954) An annotated listo of the butterflies and skippers of Cuba (Lepidoptera: Rhopalocera). Journal of the New York Entomological Society 62 (2): 113-128.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Torre S (1968) Revisión de las especies cubanas de la familia Satyridae (Lepidoptera, Rhopalocera), con la descripción de una nueva especie. Ciencias Biológicas, serie4, 3: 1–24.
- ↑ Brown F, Heineman B (1972) Jamaica and its butterflies. E. W. Classey Ltd., London xv + 478 pp.
- ↑ Alayo P, Hernández L (1987) Atlas de las mariposas diurnas de Cuba (Lepidoptera: Rhopalocera). Científico-Técnica, La Habana, 186 pp.
- ↑ Fontenla J, Rodríguez R (1990) Sistema de poblaciones de Calisto sibylla Bates, 1934 (Lepidoptera, Satyridae) en Cuba. Poeyana 395: 1-13.
- ↑ Smith D, Miller L, Miller J (1994) The Butterflies of the West Indies and South Florida. Oxford University Press, New York, 284 pp.
- ↑ Lamas G (Ed) (2004) Atlas of Neotropical Lepidoptera: Checklist: Part 4A. Hesperioidea-Papilionoidea. Vol. 5. Association for Tropical Lepidoptera, Gainesville, xxxvi + 439 pp.
- ↑ Fontenla J (1987b) Características zoogeográficas de las ropalóceras (Insecta: Lepidoptera) de Viñales, Pinar del Río, Cuba. Poeyana 339: 1-11.
Images
|