Austrodecus bamberi
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Wang2013ZooKeys349, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Wang2013ZooKeys349">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Pantopoda
Familia: Austrodecidae
Genus: Austrodecus
Name
Austrodecus Austrodecus_bamberi Wang & Huang & Lin & Zheng, 2013 sp. n. – Wikispecies link – ZooBank link – Pensoft Profile
Material examined
one male, holotype (TVG0201), DY115-20VII Station 2, SWI, 37.4654°S, 51.7213°E, 1307 m depth, TVG, 4th February 2009.
Diagnosis
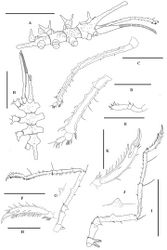
Trunk with four dorsomedian tubercles, moderately tall. All first coxae with slender dorsodistal tubercles, from anterior to posterior in formula 2: 2: 2: 1. The anterior tubercle on the first coxa of first leg is shorter than others. Cement gland dome-shaped, placed dorsally at centre of femur, on all legs. Legs with long dorsodistal spine on each major article.
Description of the holotype (male)
Size moderately large for genus; leg span 6.68 mm. Trunk slender, with many tiny papillae, completely segmented, dorsal segmentation lines raised, swollen, with four dorsomedian tubercles, moderately tall. Lateral processes separated by at least their own diameters, with tiny dorsodistal papillae. Ocular tubercle long, directed obliquely forward, slender, armed with short tubercles, without obvious eyes, tip weakly bifurcate. Proboscis typical, slender, longer than trunk length, distal part down-curved, with about 40 annulations, base swollen. Abdomen with tiny dorsal papillae, horizontal, extending to third coxae of fourth pair of legs.
Palps six-articled. First article broad, without spines or setae. Second article longest, with few short seta and spines. Articulation lines between second, third and fourth articles indistinct. Second to fourth articles with thorn-like tubercles on dorsal surfaces. Fourth article almost half length of second article, bearing four inwardly-curved spines, armed with seta. Distal two articles short, terminal article synaxial to penultimate article, both armed with fields of ventral and distal setae mostly little longer than their article diameter.
Ovigers small, four-articled. First to third articles with 1 or 2 setae. Fourth article longest, bearing several ventral and distal setae.
Legs slender, with tiny papillae and thorn-like tubercles. Major articles with long dorsodistal spine. First coxae with tall slender tubercles bearing short thorn-like tubercles and short seta, from anterior to posterior in formula 2: 2: 2: 1. Anterior tubercle on first coxa of first leg shorter than others. Second coxae longest, distally swollen, with short ventral seta and distal spines. Third coxae short, with low tubercle. Femur the longest article, with few short setae and spines. Cement glands dome-shaped, endal at centre of femur, on all legs. Spines on tibiae, tarsus and propodus decreasing in number from anterior to posterior legs. First tibiae longer than second, with fewer ventral spines. Tarsus with ventral spines, 9 on first, 7 on second, 3 on third and fourth pair. Propodus moderately curved, with 3 distal spines and 3-5 long dorsal spines (5 on first, 4 on second, 3 on third and fourth), single row of sole spines (19 on first, 13 on second, 10 on third and fourth). Main claw strong, two tiny auxiliary claws little longer than diameter of main claw.
Female and juvenile are unknown.
Measurements of holotype in mm: Trunk length (from chelifore insertion to tip of 4th lateral processes), 1.29; width across 2nd lateral processes, 0.71; proboscis length, 1.35; ocular tubercle, 0.88; abdomen, 0.47.
Length of palp articles 1 to 6 respectively: 0.06;0.73; 0.11; 0.40;0.04;0.06.
Length of oviger articles 1 to 4 respectively: 0.04; 0.07; 0.02; 0.11.
Third leg, coxa 1, 0.15; coxa 2, 0.23; coxa 3, 0.11; femur, 0.67; tibia 1, 0.56; tibia 2, 0.54; tarsus, 0.04; propodus, 0.39; claw, 0.12; auxiliary claw, 0.036.
Measurements of first leg: coxa 1, 0.14; coxa 2, 0.28; coxa 3, 0.19; femur, 0.80; tibia 1, 0.76; tibia 2, 0.65; tarsus, 0.06; propodus, 0.36; claw, 0.12; auxiliary claw, 0.029.
Etymology
This species is dedicated to Dr. Roger N. Bamber in recognition of his excellent work on the all world’s Pycnogonida.
Remarks
This species belongs to the Austrodecus tristanense section sensu Stock (1957)[1] which is characterised by 4-articled ovigers and the present of auxiliary claws. Four species are assigned to this section (Austrodecus tristanense Stock, 1955, Austrodecus goughense Stock, 1957, Austrodecus elegans Stock, 1957 and Austrodecus calvum Stock, 1991, see Child 1994[2]). Three species possess mid-dorsal trunk tubercles. Of these, Austrodecus bamberi sp. n. is most like Austrodecus calvum and Austrodecus elegans with which it shares the widely-spaced lateral processes however Austrodecus calvum does not possess mid-dorsal processes and further differs in the ratio of the lateral tubercles. Using the keys provided by Bamber and Thurston (1993)[3] and Child (1994)[2] Austrodecus bamberi keys out to Austrodecus elegans but these species are readily distinguished by the number and length of tubercles on first coxae and the much lower mid-dorsal trunk tubercles of Austrodecus elegans.
Deep-sea pycnogonids occasionally occurred in the vicinity of hydrothermal vents and deep-sea ridges, however Sericosura is the only obligate vent-associated pycnogonid genus (Bamber 2009[4]). Austrodecus bamberi was obtained on the top of ridge, close to the hydrothermal field but without evidence any obligate association. White sediment and a small amount of basalt accompanied the specimen in the TV-grab. The specimen was recovered by washing the sediment through a sieve. Corals attached to the basalt, gastropods and one squat lobster (Heteronida sp.) were also recovered from the same sample.
The sea floor appears to be predominantly composed of soft sediment.
Original Description
- Wang, J; Huang, D; Lin, R; Zheng, X; 2013: A new species of Austrodecus Hodgson, 1907 (Arthropoda, Pycnogonida, Austrodecidae) from the Southwest Indian Ridge ZooKeys, 349: 73-79. doi
Other References
- ↑ Stock J (1957) The pycnogonid family Austrodecidae. Beaufortia 6(68): 1-81.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Child C (1994) Antarctic and Subantarctic Pycnogonida: I, Ammotheidae and II, Austrodecidae. In: Cairns S (Ed) Biology of the Antarctic Seas XXIII. Antarctic Research Series 63: 1–99.
- ↑ Bamber R, Thurston M (1993) Deep water pycnogonids of the Cape Verde slope. Journal Marine Biology Association UK 73: 837-837. doi: 10.1017/S0025315400034767
- ↑ Bamber R (2009) Two new species of Sericosura Fry & Hedgpeth, 1969 (Arthropoda: Pycnogonida: Ammotheidae), and a reassessment of the genus. Zootaxa 2140: 56-68.
Images
|