Mecynothrips
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Dang2013ZooKeys345, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Dang2013ZooKeys345">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Thysanoptera
Familia: Phlaeothripidae
Name
Mecynothrips Bagnall – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Remarks
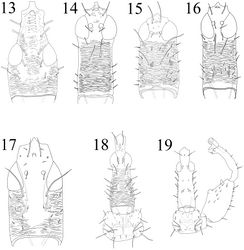
The 14 species included in this genus involve some of the largest Thysanoptera, and in the proventriculus of adults there is a prominent basket-like structure that is probably involved in crushing the fungus spores on which these species feed (Tree et al. 2010[1]). A similar structure also occurs in species of Elaphrothrips. Four species are recorded from China: Mecynothrips kanoi, Mecynothrips pugilator, Mecynothrips simplex and Mecynothrips taiwanus, of which Mecynothrips simplex is here newly recorded from China based on four females and eight males from Yunnan and Hainan Provinces. Okajima (1979)[2] described Mecynothrips taiwanus from Taiwan, and this can be distinguished from Mecynothrips pugilator by having a longer preocular projection from base of antennal segment I to anterior margin of eyes about 1.5 times as long as wide, whereas in Mecynothrips pugilator this is about as long as wide. The species Mecynothrips kanoi was described from Taiwan, but the depositary of the syntypes is unknown, and no useful characters can be taken from the simple original description. Therefore, Mecynothrips kanoi is excluded in the following key to Chinese species of Mecynothrips.
Diagnosis
Head much longer than broad, with prominent projection in front of eyes; eyes normal; 2 pairs of postoculars developed, also 1 pair of anterocellars well-developed, and 1 pair of postocellars; stylets short, V-shaped; antennae 8-segmented, segment III with 2 sensoria, IV with 4; pronotal major setae pointed or blunt, notopleural sutures usually complete, often incomplete; basantra present; mesopraesternum developed; metathoracic sternopleural sutures absent; fore wings with duplicated cilia; fore tarsal tooth present in male, absent in female, fore tibiae sometimes with seta-bearing apical tubercle in male, fore femur with a tumor or tubercles on inner margin in large male; pelta broad, with two prominent lateral lobes; abdominal tergites II–VII each with 2 or 3 pairs of sigmoid wing-retaining setae; tube smooth, without prominent lateral setae; anal setae shorter than tube.
Key to Mecynothrips species from China
Taxon Treatment
- Dang, L; Qiao, G; 2013: Review of the spore-feeding Idolothripinae from China (Thysanoptera, Phlaeothripidae) ZooKeys, 345: 1-28. doi
Other References
- ↑ Tree D, Mound L, Walter G (2010) Fungal spore-feeding by adult and larval Mecynothrips hardyi (Priesner) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae: Idolothripinae). Journal of Natural History 44: 307-316. doi: 10.1080/00222930903395150
- ↑ Okajima S (1979) Notes on the Thysanoptera from Southeast Asia VI. A new species of the Genus Mecynothrips from Taiwan (Phlaeothripidae). Transactions of the Shikoku Entomological Society 14(3-4): 127-130.
Images
|