Latest revision as of 11:48, 31 March 2014
| Notice: |
This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly.
This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Yoshimura M, Fisher B (2014) A revision of the ant genus Mystrium in the Malagasy region with description of six new species and remarks on Amblyopone and Stigmatomma (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, Amblyoponinae). ZooKeys 394 : 1–99, doi. Versioned wiki page: 2014-03-31, version 43936, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Mystrium_oberthueri&oldid=43936 , contributors (alphabetical order): PlaziBot, Pensoft Publishers.
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX:
@article{Yoshimura2014ZooKeys394,
author = {Yoshimura, Masashi AND Fisher, Brian L.},
journal = {ZooKeys},
publisher = {Pensoft Publishers},
title = {A revision of the ant genus Mystrium in the Malagasy region with description of six new species and remarks on Amblyopone and Stigmatomma (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, Amblyoponinae)},
year = {2014},
volume = {394},
issue = {},
pages = {1--99},
doi = {10.3897/zookeys.394.6446},
url = {http://www.pensoft.net/journals/zookeys/article/6446/abstract},
note = {Versioned wiki page: 2014-03-31, version 43936, https://species-id.net/w/index.php?title=Mystrium_oberthueri&oldid=43936 , contributors (alphabetical order): PlaziBot, Pensoft Publishers.}
}
RIS/ Endnote:
Wikipedia/ Citizendium:
See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Taxonavigation
Ordo: Hymenoptera
Familia: Formicidae
Genus: Mystrium
Name
Mystrium oberthueri Forel, 1897 – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Mystrium oberthueri Forel, 1897. MADAGASCAR. Syntypes: one worker (as major) and two ergatoid queens (as minor) [lectotype is designated below].
- Mystrium oberthueri: Menozzi 1929[1] (in part?: uncertain male identification)
- Mystrium oberthueri (Not) (male): Emery 1899[2].
- Mystrium rogeri (male): Forel 1899[3].
Lectotype
[here designated]. Worker: CASENT0101993, MADAGASCAR, Insel Ste. Marie (Island of Sainte Marie), Perrot [MHNG: examined].
Worker
Description. Measurements: lectotype. HL 2.40, HW 2.61, SL 1.80, ML 2.92, HD 1.67, WL 2.79, PnW 1.39, PpW 1.21, PtW 1.18, PtL 0.81, CI 108.7, SI 69.0, MI 111.8, PpI 87.4, PtI 144.9.
HL 2.00–2.58, HW 2.12–2.76, SL 1.55–1.96, ML 2.39–3.17, HD 1.33–1.69, WL 2.43–2.96, PnW 1.17–1.38, PpW 1.02–1.29, PtW 1.00–1.32, PtL 0.67–0.81, CI 104.4–108.5, SI 68.8–74.9, MI 106.9–122.9, PpI 87.2–93.8, PtI 139.5–163.2 (10 specimens measured).
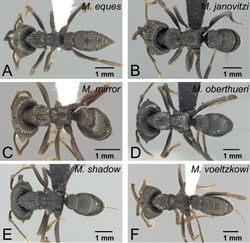
Posterolateral corner of head moderately expanding posteriorly. Posterior face of vertex forming almost right angle with dorsal face on median line of head, so that declivity of vertex on lateral part as steep as on median part. Whole region of vertex finely striated. Eye moderately small. Anterior margin of clypeus straight or weakly convex with long conical setae. Genal tooth of head relatively long, as long as lateral lobe of clypeus. Masticatory surface of mandible almost invisible in full-face view, and width of dorsal surface of mandible almost identical from mandibular shaft to distal portion. Second maxillary palpomere longer than third. First flagellomere (third antennal segment) about 1.2–1.5× length of pedicel (second antennal segment). Strong, deep longitudinal striae regularly impressed on whole central part of pronotal dorsum. Strong, deep longitudinal striae impressed on lateral surface of pronotum. Mesonotum differentiated from propodeum in dorsal view, length slightly shorter than that of propodeum. Metanotal groove shallowly and gently impressed in lateral view. Metapleural gland bulla moderately developed, and propodeal declivity in lateral view almost straight. Petiole widened on posterior 1/3 and gently narrowing anteriorly in dorsal view, anterior margin straight to gently rounded and often edged by thick striae.
Body color black.
Ergatoid queen
Description. Measurements: HL 1.40–1.93, HW 1.46–1.96, SL 1.07–1.47, ML 1.49–2.00, HD 1.00–1.35, WL 1.92–2.56, PnW 0.83–1.11, PpW 0.85–1.13, PtW 0.81–1.07, PtL 0.53–0.70, CI 101.6–108.6, SI 71.6–76.7, MI 96.3–108.8, PpI 96.0–104.4, PtI 149.1–177.1 (10 specimens measured).
Wings vestigial and reduced to small but distinct appendages. Wing sclerites undeveloped. Posterolateral corner of head moderately expanding posteriorly, expansion not differentiated from that in workers. Posterior face of vertex forming almost a right angle with dorsal face on median line of head, so that declivity of vertex on lateral part as steep as on median part. Ventral half of vertex sculptured. Eye small but distinct. Ocelli absent. Anterior margin of clypeus almost straight with long to moderate conical setae. Anterolateral portion of head with short spine. Masticatory margin of mandible almost invisible in full-face view, and dorsal surface on distal portion as wide as that on mandibular shaft. Spatulate seta present on basal side of each basal denticle on masticatory margin of mandible. First flagellomere (third antennal segment) long, about 1.2-1.5× length of pedicel (second antennal segment). Setae on pronotum distinctly spatulate, widened distally with sharp or blunt apex. Metapleural gland bulla moderately developed, not expanding dorsally to propodeal spiracle, so that propodeal declivity in lateral view weakly convex and rounded posteriorly on its ventral 1/3. Petiole relatively long in dorsal view, about 0.8× length of abdominal segment III.
Body color blackish to reddish brown.
Male
Description. Measurements: HL 1.44, HW 2.09, SL 0.62, EL 0.95, WL 3.55, MnW 1.94, CI 145.1, SI 29.6, EI 66.2, MnI 92.9 (1 specimen measured).
Eye moderately large, occupying 0.6× of head length. Ocelli relatively distant from dorsal margin of head in full-face view. Dorsal margin of head in full-face view straight. Both anterior and lateral ocelli small. Lateral ocellus small and distant from eye: distance between these more than 1.5× maximum diameter of lateral ocellus. Posterior face of vertex not clearly differentiated from dorsal face, so that vertex almost continuously rounded. Palpal formula 4,3. First maxillary palpomere flattened and distinctly wider than second segment. Second maxillary palpomere longer than third. Notauli clearly impressed on mesoscutum. Petiole in dorsal view thin, 0.8× as long as abdominal tergite III. Petiolar dorsum covered with shallow, irregular punctures. Abdominal tergum VIII without deep punctures, almost smooth.
Distal portion of abdominal sternum IX smooth and not punctured. Basal ring moderately long, expanding basoventrally. Telomere distinctly extending distally farther than digitus. Basoventral expansion of aedeagus moderately developed basoventrally, longer than dorsal extension. Ventral margin of aedeagus gently convex in lateral view. Aedeagus moderately narrowing distally and distal portion rounded.
On forewing, cu-a located far basal from junction of Media (M) and Cubitus (Cu).
Body color reddish brown to black.
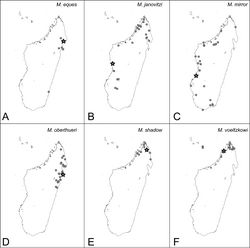
Distribution
MADAGASCAR: as in Figure 56D.
Additional material examined
In addition to the type material, specimens from the following localities were examined in this study: MADAGASCAR. Antsiranana. Forêt d’ Antsahabe, 11.4 km 275° W Daraina (-13.21167°, 49.55667°), tropical dry forest, 550 m alt.; Makirovana forest (-14.17066°, 49.95409°), rainforest, 415 m alt.; Parc National de Marojejy, Manantenina River, 27.6 km 35° NE Andapa, 9.6 km 327° NNW Manantenina (-14.435°, 49.76°), rainforest, 775 m alt.; 28.0 km 38° NE Andapa, 8.2 km 333° NNW Manantenina (-14.43667°, 49.775°), rainforest, 450 m alt.; Marojejy R.N.I. #12 (-14.43583°, 49.76056°), rainforest, 610 m alt.; Forêt Ambanitaza, 26.1 km 347° Antalaha (-14.67933°, 50.18367°), rainforest, 240 m alt.; 1 km W Andampibe, Cap Masoala (-15.69361°, 50.18139°), lowland rainforest, 125 m alt.; Fotodriana, Cap Masoala (-15.69694°, 50.27028°), lowland rainforest, 25 m alt.; Toamasina. Montagne d’Anjanaharibe, 18.0 km 21° NNE Ambinanitelo (-15.18833°, 49.615°), rainforest, 470 m alt.; Montagne d’Akirindro 7.6 km 341° NNW Ambinanitelo (-15.28833°, 49.54833°), rainforest, 600 m alt.; 19 km ESE Maroantsetra (-15.48333°, 49.9°), rainforest, 350 m alt.; 5.3 km SSE Ambanizana, Andranobe (-15.66667°, 49.96667°), rainforest, 425 m alt.; 6.3 km S Ambanizana, Andranobe (-15.6813°, 49.958°), rainforest, 5 m alt.; 6.3 km S Ambanizana, Andranobe (-15.68131°, 49.958°), rainforest, 25 m alt.; Parc National Mananara-Nord, 7.1 km 261° Antanambe (-16.455°, 49.7875°), rainforest, 225 m alt.; Res. Ambodiriana, 4.8 km 306° Manompana, along Manompana river (-16.67233°, 49.70117°), rainforest, 125 m alt.; Réserve Spéciale Ambatovaky, Sandrangato river (-16.7633°, 49.26692°), rainforest, 520 m alt.; (-16.77274°, 49.26551°), rainforest, 450 m alt.; (-16.7755°, 49.26427°), rainforest, 430 m alt.; (-16.81745°, 49.2925°), rainforest, 400 m alt.; (-16.81753°, 49.29498°), rainforest, 360 m alt.; Ile Sainte Marie, Forêt Kalalao, 9.9 km 34° Ambodifotatra (-16.9225°, 49.88733°), rainforest, 100 m alt.; Réserve Forestière Tampolo, 95.2 km N Toamasina (-17.27808°, 49.42853°), littoral rainforest, 20 m alt.; S.F. Tampolo, 10 km NNE Fenoarivo Atn. (-17.2825°, 49.43°), littoral rainforest, 10 m alt.; Bridge at Onibi, NW of Mahavelona (-17.65°, 49.46667°), in clay forest; Mahavelona (Foulpointe) (-17.66667°, 49.5°), Forest; Parc National de Zahamena, Besaky River (-17.75244°, 48.85321°), rainforest, 760 m alt.; Sahavorondrano River (-17.75257°, 48.85725°), rainforest, 765 m alt.; Onibe River (-17.75908°, 48.85468°), rainforest, 780 m alt.; Reserve Betampona, Camp Vohitsivalana, 37.1 km 338° Toamasina (-17.88667°, 49.2025°), rainforest, 520 m alt.; Réserve Naturelle Betampona, 34.1 km 332° Toamasina (-17.916135°, 49.20185°), rainforest, 550 m alt.; Réserve Nationale Intégrale Betampona, Betampona 35.1 km NW Toamasina (-17.91801°, 49.20074°), rainforest, 500 m alt.; Reserve Betampona, Camp Rendrirendry 34.1 km 332° Toamasina (-17.924°, 49.19967°), rainforest, 390 m alt.; F.C. Sandranantitra (-18.04833°, 49.09167°), rainforest, 450 m alt.; F.C. Andriantantely (-18.695°, 48.81333°), rainforest, 530 m alt.; Sahafina forest 11.4 km W Brickaville (-18.81445°, 48.96205°), rainforest, 140 m alt. Mahajanga. Réserve Spéciale Marotandrano, Marotandrano 48.3 km S Mandritsara (-16.28322°, 48.81443°), transition humid forest, 865 m alt.
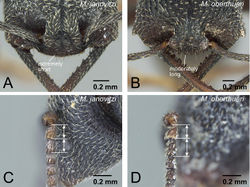
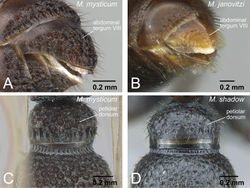
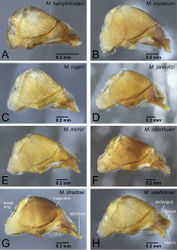
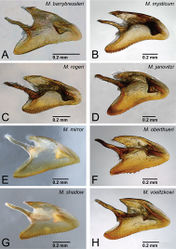
The worker of Mystrium oberthueri is easily distinguished from that of other Mystrium species by the combination of the following characters: strong, deep, and thick longitudinal sculpture on the dorsal and lateral surface of pronotum (Fig. 17B); straight anteromedial margin of the clypeus (Fig. 18A); a sharper angle between the dorsal and posterior faces of the vertex on the median line of the head (Fig. 16A). The queen of Mystrium oberthueri is differentiated from other queens of Mystrium species by the vestigial wings reduced to small appendages with undeveloped wing sclerites (ergatoid: as in Fig. 25D), the posterior face of the vertex forming approximately a right angle with its dorsal face on the median line of the head (as in Fig. 21A), straight anterior clypeal margin (Fig. 22B), and moderately developed clypeal conical setae (Fig. 23B). The male of Mystrium oberthueri can be separated from the other known Mystrium males by its smooth abdominal tergum VIII (as in Fig. 28), small lateral ocelli situated distant from posterior margin of head in full-face view, and straight dorsal margin of head in full-face view (Fig. 30A). We should note that the current male character diagnoses may not be able to distinguish between Mystrium oberthueri and Mystrium eques, which is not yet known from the male caste and may be quite similar to Mystrium oberthueri.
The lectotype for Mystrium oberthueri is designated. According to Forel (1897)[4], a single major worker and multiple ergatoid queens (as minor workers) were used for the original description of Mystrium oberthueri. We confirmed one worker and one ergatoid queen in the Forel collection in MHNG and one ergatoid queen in MCZC, all of which are labeled with the location “Ste. Marie Madagascar.” The single worker was chosen as the new representative specimen.
Although worker descriptions for Mystrium oberthueri are reliable, male descriptions of this species in previous papers are problematic. The original description by Forel (1897)[4] did not include males. Later male descriptions were given by Emery (1899)[2] and Menozzi (1929)[1]. As in the cases of Mystrium mysticum and Mystrium rogeri, Emery’s and Menozzi’s descriptions of the male of Mystrium oberthueri seem to be based on specimens not associated with conspecific workers. We did not examine the actual male specimens they used, and cannot be sure that these descriptions are for the actual male of Mystrium oberthueri. Emery mentioned Forel’s description (Forel 1899[3]) of Mystrium rogeri in the same paper. We have confirmed the male described as Mystrium rogeri was the actual Mystrium oberthueri; however, Emery (1899)[2] did not mention this problem. Moreover, Emery listed smaller body size as a character able to distinguish the male of Mystrium oberthueri from that of Mystrium mysticum; however, according to our measurements, Mystrium oberthueri is the largest of the Mystrium males (Mystrium oberthueri: HW>2.00 mm vs. other known males: HW<1.88 mm). We believe that Emery’s male description for Mystrium oberthueri is doubtful, even though we have not been able to determine the males described in either Mystrium oberthueri or Mystrium mysticum in Emery (1899)[2]. Second, Menozzi (1929)[1] examined all types in the Forel collection, including those of Mystrium rogeri. However, he did not mention anything in the male description of Mystrium oberthueri about the male in the syntypes of Mystrium rogeri. Hence, the male description of the Mystrium oberthueri in Menozzi (1929)[1] is also not likely to be the true Mystrium oberthueri, although it probably is a male in the voeltzkowi species group.
We describe a new species, Mystrium eques, with a worker similar to that of Mystrium oberthueri. As we have already mentioned in the section of Mystrium eques, the unknown male of Mystrium eques is likely to be quite similar to that of Mystrium oberthueri, and the current male diagnosis for Mystrium oberthueri may be insufficient to distinguish these two males (see Mystrium eques).
Material identified as Mystrium oberthueri in Molet et al. (2009)[5] and Bouchet et al. (2013)[6] is confirmed here.
Taxon Treatment
- Yoshimura, M; Fisher, B; 2014: A revision of the ant genus Mystrium in the Malagasy region with description of six new species and remarks on Amblyopone and Stigmatomma (Hymenoptera, Formicidae, Amblyoponinae) ZooKeys, 394: 1-99. doi
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Menozzi C (1929) Revisione delle formiche del genere Mystrium Roger. Zoologischer Anzeiger 82: 518-536.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Emery C (1899) Formiche di Madagascar raccolte dal Sig. A. Mocquerys nei pressi della Baia di Antongil (1897–1898). Bullettino della Societa Entomologica Italiana 31: 263-290.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Forel A (1899) Trois notices myrmécologiques. Annales de la Société Entomologique de Belgique 43: 303-310.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Forel A (1897) Ameisen aus Nossi-Bé, Majunga, Juan de Nova (Madagaskar), den Aldabra-Inseln und Sansibar, gesammelt von Herrn Dr. A. Voeltzkow aus Berlin. Mit einem Anhang über die von Herrn Privatdocenten Dr. A. Brauer in Marburg auf den Seychellen und von Herrn Perrot auf Ste. Marie (Madagaskar) gesammelten Ameisen. Abhandlungen der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft 21: 185-208.
- ↑ Molet M, Fisher B, Ito F, Peeters C (2009) Shift from independent to dependent colony foundation and evolution of ‘multi-purpose’ ergatoid queens in Mystrium ants (subfamily Amblyoponinae). Biological journal of the Linnean Society 98: 198-207. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01257.x
- ↑ Bouchet D, Peeters C, Fisher B, Molet M (2013) Both female castes contribute to colony emigration in the polygynous ant Mystrium oberthueri. Ecological Entomology 38: 408-417. doi: 10.1111/een.12033
Images
| Figure 1. Colonies of Mystrium. A Mystrium oberthueri B Mystrium voeltzkowi. A a cocoon and a worker B larvae, workers, and ergatoid queens. Photos by Alex Wild. |
|