Difference between revisions of "Scytinostroma boidinii"
m (Imported from MycoKeys) |
m (1 revision imported) |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 16:05, 13 June 2023
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Li2023MycoKeys98, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Li2023MycoKeys98">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Russulales
Familia: Peniophoraceae
Genus: Scytinostroma
Name
Scytinostroma boidinii Yue Li, S.L. Liu & S.H. He sp. nov. – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
Type
China, Beijing, Mentougou District, Xiaolongmen Forest Park, on dead angiosperm branch, 28 August 2020, He 6911 (BJFC 033860, holotype).
Etymology
Named to honor Dr. Jacques Boidin (Lyon, France) who contributed much to the taxonomy of Scytinostroma.
Fruiting body
Basidiomes annual, resupinate, widely effused, closely adnate, inseparable from substrate, membranaceous to coriaceous, first as small patches, later confluent up to 9 cm long, 3.5 cm wide, up to 300 µm thick in section. Hymenophore smooth, pale yellow (4A3), greyish yellow (4B4) to greyish orange [5B(3–4)], unchanged in KOH, not cracked; margin thinning out, adnate, fimbriate, white or concolorous with hymenophore surface. Context pale yellow.
Microscopic structures
Hyphal system dimitic. Context thickening, compact. Generative hyphae rare, scattered, simple-septate, colorless, slightly thick-walled, 2–3 µm in diam., IKI–, CB–. Skeletal hyphae dominant, colorless to yellow, distinctly thick-walled, moderately branched, 1.5–2 µm in diam., dextriniod, CB+. Catahymenium composed of skeletal hyphae, gloeocystidia, basidia and basidioles. Skeletal hyphae abundant, similar to those in the context, but strongly dextrinoid, dichotomous-branched with acute tips, 1–1.5 µm wide at lowest part. Gloeocystidia abundant, subcylindrical to subfusiform, colorless, slightly thick-walled, with or without contents, weakly SA+, 50–80 × 5–10 µm. Basidia subclavate to subcylindrical, thin-walled, colorless, smooth, with four sterigmata and a basal simple septum, 30–50 × 4–7 µm; basidioles in shape similar to basidia, but slightly smaller. Basidiospores subglobose, with a distinct apiculus, thin-walled, colorless, smooth, occasionally with oil-drops, amyloid, CB–, (4.5–) 5–5.5 (–6.5) × (4–) 4.5–5.5 (–6.2) µm, L = 5.1 µm, W = 5.0 µm, Q = 1.02–1.04 (n = 60/2).
Additional specimens examined
China, Beijing, Mentougou District, Lingshan Scenic Spot, on dead angiosperm branch, 10 April 2022, He 7465a (BJFC 038600) & He 7465b (BJFC 038601); Gansu Province, Tianshui County, Dangchuan Forest Farm, on dead Quercus tree, 9 August 2015, He 2499 (BJFC 020952); Hebei Province, Xinglong County, Wulingshan Nature Reserve, on dead angiosperm branch, 2 September 2017, He 4985 (BJFC 024503); Jilin Province, Jiaohe County, forestry experimental area, on fallen angiosperm trunk, 3 September 2017, He 5138 (BJFC 024656).
Notes
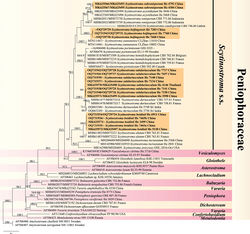
Scytinostroma boidinii is characterized by the relatively long gloeocystidia and subglobose basidiospores. In the phylogenetic tree (Fig. 1), S. boidinii formed a distinct lineage sister to S. alutum Lanq., which differs in having cracked basidiomes, slightly larger basidiospores (5–7 × 5–7.5 µm) and a distribution in France, Spain and Pakistan (Boidin and Lanquetin 1987[1]; Bernicchia and Gorjón 2010[2]). Scytinostroma yunnanense C.L. Zhao from Yunnan Province, southwestern China, has similar-sized basidiospores (4.5–5.5 × 4.2–5.2 µm) to S. boidinii, but differs in having white to cream hymenophore, smaller gloeocystidia (28–33 × 4–5 µm) and smaller basidia (21–28 × 4–5.5 µm, Wang et al. 2020[3]).
Original Description
- Li, Y; Xu, W; Liu, S; Yang, N; He, S; 2023: Species diversity and taxonomy of Scytinostroma sensu stricto (Russulales, Basidiomycota) with descriptions of four new species from China MycoKeys, 98: 133-152. doi
Images
|
Other References
- ↑ Boidin J, Lanquetin P (1987) Le genre Scytinostroma Donk.Bibliotheca Mycologica114: 1–130.
- ↑ Bernicchia A, Gorjón S (2010) Corticiaceae s.l. Fungi Europaei 12. Edizioni Candusso. Alassio, Italia.
- ↑ Wang H, He X, Zhao C (2020) Scytinostroma yunnanense sp. nov. (Russulales, Basidiomycota) evidenced by morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analyses in China.Phytotaxa451: 145–153. https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.451.2.4