Difference between revisions of "Bavia capistrata"
m (1 revision imported) |
m (Imported from ZooKeys) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 18:36, 9 November 2016
| Notice: | This page is derived from the original publication listed below, whose author(s) should always be credited. Further contributors may edit and improve the content of this page and, consequently, need to be credited as well (see page history). Any assessment of factual correctness requires a careful review of the original article as well as of subsequent contributions.
If you are uncertain whether your planned contribution is correct or not, we suggest that you use the associated discussion page instead of editing the page directly. This page should be cited as follows (rationale):
Citation formats to copy and paste
BibTeX: @article{Cao2016ZooKeys, RIS/ Endnote: TY - JOUR Wikipedia/ Citizendium: <ref name="Cao2016ZooKeys">{{Citation See also the citation download page at the journal. |
Ordo: Araneae
Familia: Salticidae
Genus: Bavia
Name
Bavia capistrata (C.L. Koch, 1846) – Wikispecies link – Pensoft Profile
- Maevia capistrata C.L. Koch, 1846: 76, fig. 1331 (♂).
- Bavia capistrata : Żabka 1988[1]: 435, figs 37–39 (♂, removed from synonymy with Evarcha flavocincta).
Material examined
1♂, CHINA, Yunnan, Mengla County, Menglun Town, Xishuangbanna Nature Reserve: nearby fish pond (21°57.883'N, 101°12.147'E, 839 m), ravine rainforest, 15 August 2011, Q. Zhao & Z. Chen leg.; 1♀, CHINA, Yunnan, Mengla County, Xiaolongha Village, Xishuangbanna Nature Reserve: Biological diversity corridor (21°24.265'N, 101°37.300'E, 653 m), seasonal rainforest, 27 June 2012, Q. Zhao & Z. Chen leg.
Diagnosis
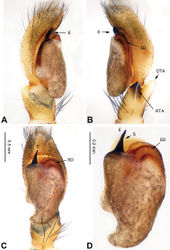
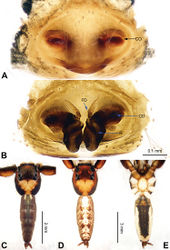
Differs from the closely related Bavia aericeps Simon, 1877 (see Żabka 1988[1]: figs 29–36) by the tibia with a distinct dorsal apophysis (Fig. 5B) and serrated embolus (Fig. 5D). The females differ from Bavia aericeps by the horizontal position of the copulatory openings (Fig. 6A) vs. the inclined copulatory organs and the arc-shaped posterior epigynal margin (Fig. 6A) vs. triangular.
Description
Male. Well described by Żabka (1988)[1].
Female. Total length 8.70, CL 3.44, CW 2.75, AL 5.26, AW 1.92. Eye measurements: AME 0.69, ALE 0.28, PME 0.06, PLE 0.29, AER 2.00, PER 2.00, EFL 1.88. Clypeus 0.16 high. Legs: I 6.92 (2.13, 1.35, 1.75, 1.14, 0.55); II 5.50 (1.70, 1.06, 1.26, 0.98, 0.50); III 5.33 (1.60, 0.95, 1.00, 1.19, 0.59); IV 9.09 (2.25, 1.00, 1.74, 1.74, 0.63).
Carapace reddish-brown, lighter dorsally, ocular area dark brown (Fig. 6C) with white setae. Chelicerae dark brown. Maxillae elongate with white tips. Labium dark brown with white tips. Sternum yellowish. Abdomen long with light broad median stripe and grey margins. Venter with few longitudinal rows of white dots. Spinnerets brownish grey. Legs I more robust and darker than others. Legs II–IV yellowish. Spination of leg I: femur d2-1-0; tibia v2-2-2, metatarsus p2-0-2. Epigyne strongly sclerotised along the posterior midline margin (Fig. 6A). Copulatory openings slit shaped, with strongly sclerotised edges. Distance between the openings subequal to 1.5 times the length of a copulatory opening. Copulatory ducts short and strongly sclerotised, receptacles close to each other. The length and width of receptacles subequal to the copulatory ducts. Fertilisation ducts located at the joined part of the copulatory ducts and receptacles (Fig. 6B).
Distribution
Malaysia to Australia, Pacific Islands, and South China.
Remark
Female of Bavia capistrata is described for the first time.
Taxon Treatment
- Cao, Q; Li, S; Żabka, M; 2016: The jumping spiders from Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China (Araneae, Salticidae) ZooKeys, (630): 43-104. doi
Images
|
Other References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Żabka M (1988) Salticidae (Araneae) of Oriental, Australian and Pacific regions, III. Annales Zoologici, Warszawa 41: 421–479.