Difference between revisions of "Mycological teaching diagrams by Meike Piepenbring"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
These diagrams have been created for teaching of mycology and phytopathology. They are shared here in order to extend our knowledge on fungi, especially those living in the tropics. | These diagrams have been created for teaching of mycology and phytopathology. They are shared here in order to extend our knowledge on fungi, especially those living in the tropics. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.2 phylogeny fungi plants animals algae 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Phylogeny of fungi (names in bold), simplified (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Phylogeny of fungi (names in bold), simplified | Phylogeny of fungi (names in bold), simplified | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.5 Fungi cellular organisation hypha yeast spore amoeba plasmodium flagellation opisthokont 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Cellular structures of fungi and algae (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Cellular structures of fungi and algae | Cellular structures of fungi and algae | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.8 Fungi hypha asexual growth spore chlamydospore yeast 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Vegetative development starting from a hypha (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Vegetative development starting from a hypha | Vegetative development starting from a hypha | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.9 life cycle sporothallus gametothallus diplohaplontic schematical 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Life cycle, generations and nuclear stages (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Life cycle, generations and nuclear stages | Life cycle, generations and nuclear stages | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.10 Pilze Fungi Befruchtung Gametangien Gameten Isogamie Oogamie Spermatisierung Somatogamie 2021 en(M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Types of fertilization (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Types of fertilization | Types of fertilization | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.2 Fungi life cycle with dikaryotic phase Basidiomycota Ascomycota 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Life cycle with dikaryotic stage, Ascomycota Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Life cycle with dikaryotic stage, Ascomycota Basidiomycota | Life cycle with dikaryotic stage, Ascomycota Basidiomycota | ||
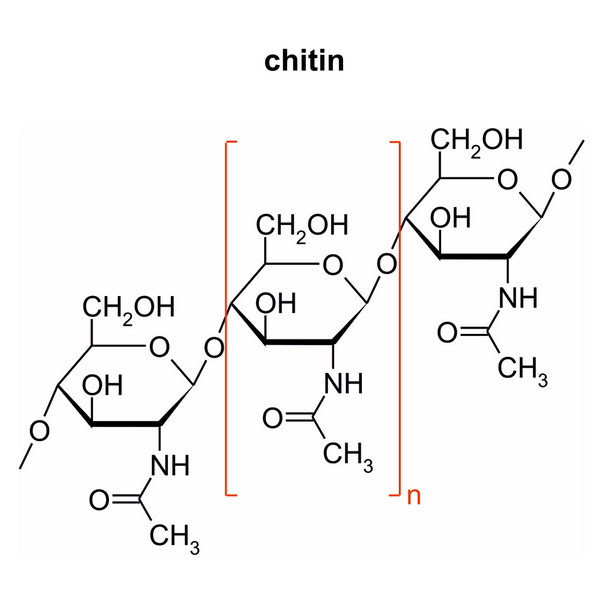
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Fungi chemical structure chitin.png|none|600px|Chitin, Fungi (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Chitin, Fungi | Chitin, Fungi | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.1 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricomycotina Ustilaginomycotina Pucciniomycotina phylogeny 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Phylogeny Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Phylogeny of Basidiomycota | Phylogeny of Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.3 Fungi Basidiomycota clamp development hypha dikaryon 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Development of clamp connection (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Development of a clamp connection | Development of a clamp connection | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.6 Fungi Basidiomycota Basidientypen Holobasidie Phragmobasidie Teleutospore 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Types of basidia (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Types of basidia | Types of basidia | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.5 Fungi Basidiomycota basidium basidiospore ballistospore Bullers drop catapult mechanism 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Discharge of ballistospore (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Discharge of a ballistospore | Discharge of a ballistospore | ||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.81 Fungi Basidiomycota jelly fungi basidiospores germination Heterobasidiomycetes 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Development starting from a basidiospore (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Development starting from a basidiospore | Development starting from a basidiospore | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.7 Fungi septal pore Woronin body dolipore parenthesome 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Pores in septa of hyphae of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Pores in septa of hyphae of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota | Pores in septa of hyphae of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.8 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricomycotina life cycle 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Life cycle Basidiomycota basidium (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Life cycle of Basidiomycota, basidium | Life cycle of Basidiomycota, basidium | ||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.9 Fungi Basidiomycota fruiting body basidioma agaricoid polyporoid hydnoid corticioid cyphelloid 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Types of fruiting bodies, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Types of fruiting bodies, Basidiomycota | Types of fruiting bodies, Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.15 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales basidioma lamellae stipe 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Connections of a lamella to the stipe, Agaricales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Connections of a lamella to the stipe, Agaricales Basidiomycota | Connections of a lamella to the stipe, Agaricales Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.17 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales Amanita angiocarpic 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Hemiangiocarpic fruiting body, Agaricales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Hemiangiocarpic fruiting body of ''Amanita'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | Hemiangiocarpic fruiting body of ''Amanita'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 132: | Line 132: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.21 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales life cycle 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Life cycle of Agaricus sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Life cycle of ''Agaricus'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | Life cycle of ''Agaricus'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 141: | Line 141: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.35 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales leaf-cutting leafcutter ants Attamyces bromatium gongylidium 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|C 2b leaf-cutting ants, bromatium, Agaricales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Bromatium of leaf-cutting ants, asexual stage of Agaricales Basidiomycota | Bromatium of leaf-cutting ants, asexual stage of Agaricales Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.32 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales Termitomyces termite mound fungal garden termite fungi mycotete 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|C 2e termite nest, Termitomyces sp., Termitosphaera sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Termite nest, ''Termitomyces'' sp., ''Termitosphaera'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | Termite nest, ''Termitomyces'' sp., ''Termitosphaera'' sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 169: | Line 169: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb1.4 ectomycorrhiza schematical macroscopic Boletales Tuber 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|C 5a ectomycorrhizae in their habitat, Boletales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Ectomycorrhizae in their habitat, Boletales Basidiomycota (left hand side) and Tuberales Ascomycota (right hand side) | Ectomycorrhizae in their habitat, Boletales Basidiomycota (left hand side) and Tuberales Ascomycota (right hand side) | ||
| Line 176: | Line 176: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.41 ectomycorrhiza root section microscopic hyphal sheath Hartig net 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|C 5b ectomycorrhiza anatomy, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Ectomycorrhiza anatomy, Basidiomycota | Ectomycorrhiza anatomy, Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 183: | Line 183: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb5.12 mycorrhiza mycoheterotrophy Monotropa Cryptothallus mirabilis Voyria Glomus Tulasnella Tricholoma 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|C 6b Monotropa uniflora, mycoheterotrophic (erroneously called saprotrophic) plant with its fungus in the habitat (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
''Monotropa uniflora'', mycoheterotrophic (erroneously called saprotrophic) plant with its fungus in the habitat | ''Monotropa uniflora'', mycoheterotrophic (erroneously called saprotrophic) plant with its fungus in the habitat | ||
| Line 195: | Line 195: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.51 Fungi Basidiomycota Polyporales skeletal hypha 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Skeletal hyphae of Lentinus sp., Polyporales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Skeletal hyphae of ''Lentinus'' sp., Polyporales Basidiomycota | Skeletal hyphae of ''Lentinus'' sp., Polyporales Basidiomycota | ||
| Line 205: | Line 205: | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.66 Fungi Basidiomycota gasteromycetation secotioid gasteroid hypogeous truffle 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Types of fruiting bodies of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
| + | [[File:Abb2.69 Fungi Basidiomycota Agaricales gasteroid fruiting body Bovista Lycoperdon Tulostoma Cyathus 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px]] | ||
Types of fruiting bodies of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | Types of fruiting bodies of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.67 Fungi Basidiomycota Gasteromycetes belly fung basidia Lycoperdon Rhizopogon Scleroderma Clathrus 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Types of basidia of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Types of basidia of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | Types of basidia of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.79 Fungi Basidiomycota Geastrales Geastrum fruiting body forniculate Sphaerobolus 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Fruiting bodies of Geastraceae, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Fruiting bodies of Geastraceae, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | Fruiting bodies of Geastraceae, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.75 Fungi Basidiomycota Phallales fruiting body Phallus Clathrus Staheliomyces Laternea receptaculum 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Fruiting bodies of Phallales, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Fruiting bodies of Phallales, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | Fruiting bodies of Phallales, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.83 Fungi Basidiomycota Auriculariales Tremellales basidia septal pores systematics 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Classification of Auriculariales and Tremellales, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Classification of Auriculariales and Tremellales, Basidiomycota | Classification of Auriculariales and Tremellales, Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.85 Fungi Basidiomycota Auriculariales Exidiopsis basidia 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Hymenium with basidium and basidiospores of Exidiopsis laccata, Auriculariales Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Hymenium with basidium and basidiospores of ''Exidiopsis laccata'', Auriculariales Basidiomycota | Hymenium with basidium and basidiospores of ''Exidiopsis laccata'', Auriculariales Basidiomycota | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Abb2.101 Fungi Basidiomycota Ustilaginomycotina smut fungi phylogeny 2021 (M. Piepenbring).png|none|600px|Phylogeny of smut fungi (black, bold) and closely related groups, Basidiomycota (diagram by M. Piepenbring)]] |
Phylogeny of smut fungi (black, bold) and closely related groups, Basidiomycota | Phylogeny of smut fungi (black, bold) and closely related groups, Basidiomycota | ||
Revision as of 04:17, 29 November 2021
(These diagrams are also available in Spanish)
Contents
Introduction
These diagrams have been created for teaching of mycology and phytopathology. They are shared here in order to extend our knowledge on fungi, especially those living in the tropics.
Phylogeny of fungi (names in bold), simplified
Cellular structures of fungi and algae
Vegetative development starting from a hypha
Life cycle, generations and nuclear stages
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Types of fertilization
Different types of fertilization. Long, red arrows indicate direction of movement. Short red arrows indicate growth by which compatible cells get in contact with each other and fuse. Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Groups of Fungi
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Divisions of true fungi, Fungi, simplified
Life cycle with dikaryotic stage, Ascomycota Basidiomycota
Chitin, Fungi
Basidiomycota
Phylogeny of Basidiomycota
Development of a clamp connection
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Types of basidia
Discharge of a ballistospore
Based on Money (1998), simplified.
Money, N.P. 1998. More g’s than the space shuttle: ballistospore discharge. Mycologia 90: 547-558.
Development starting from a basidiospore
Pores in septa of hyphae of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota
Life cycle of Basidiomycota, basidium
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Types of fruiting bodies, Basidiomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Concepts of Agaricales and Polyporales, Basidiomycota
Connections of a lamella to the stipe, Agaricales Basidiomycota
Hemiangiocarpic fruiting body of Amanita sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota
Modified after diagrams by Yang Zhu-Liang; with permission.
Life cycle of Agaricus sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Bromatium of leaf-cutting ants, asexual stage of Agaricales Basidiomycota
Escovopsis weberi, parasite of the fungus cultivated by leaf-cutting ants, conidiophore with conidia, asexual form of Hypocreales, Ascomycota
Termite nest, Termitomyces sp., Termitosphaera sp., Agaricales Basidiomycota
Diagram on the left hand side based on Heim (1977) and Buyck (1994).
Buyck, B. 1994. Ubwoba: les champignons comestibles de l'Ouest du Burundi. Publ. Agric. 34.
Heim, R. 1977. Termites et champignons. Les champignons termitophiles d´Afrique Noire et d´Asie méridionale. Société Nouvelle des Éditions Boubée, Paris.
Drawing on the right hand side based on a drawing by Roland Kirschner, used with permission.
Hyphae with conidia of Moniliophthora roreri, asexual stage of Agaricales Basidiomycota
Ectomycorrhizae in their habitat, Boletales Basidiomycota (left hand side) and Tuberales Ascomycota (right hand side)
In collaboration with Ingrid Kottke.
Ectomycorrhiza anatomy, Basidiomycota
In collaboration with Ingrid Kottke.
Monotropa uniflora, mycoheterotrophic (erroneously called saprotrophic) plant with its fungus in the habitat
In collaboration with Ingrid Kottke.
Types of hymenophores of Polyporales, Basidiomycota
Skeletal hyphae of Lentinus sp., Polyporales Basidiomycota
Hypha with conidia of Allescheriella crocea, asexual form of Basidiomycota
Types of fruiting bodies of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota
Types of basidia of gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota
Fruiting bodies of Geastraceae, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota
Fruiting bodies of Phallales, gasteromycetes, Basidiomycota
Classification of Auriculariales and Tremellales, Basidiomycota
Hymenium with basidium and basidiospores of Exidiopsis laccata, Auriculariales Basidiomycota
Phylogeny of smut fungi (black, bold) and closely related groups, Basidiomycota
Basidia of smut fungi, Basidiomycota
Homothallic basidia of smut fungi, Basidiomycota
Sori of smut fungi, Basidiomycota
Life cycle of Ustilago maydis on corn, Ustilaginales Basidiomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Tilletia ayresii on Panicum maximum, Tilletiales Basidiomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Teliospore ball of Narasimhania alismatis in a leaf of Sagittaria guyanensis, Doassansiales Basidiomycota
Teliospores, a basidium, and dikaryotic cells of Entyloma sp. in a leaf, Entylomatales Basidiomycota
Fruiting body with elaters and basidia of Graphiola spp., Exobasidiales Basidiomycota
Life cycle of Graphiola phoenicis, Exobasidiales Basidiomycota
Based on Cole (1983) and Oberwinkler et al. (1982).
Cole, G.T. 1983. Graphiola phoenicis: a taxonomic enigma. Mycologia 75: 93-116.
Oberwinkler, F., R.J. Bandoni, P. Blanz, G. Deml & L. Kisimova-Horovitz. 1982. Graphiolales: Basidiomycetes parasitic on palms. Pl. Syst. Evol. 140: 251-277.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Teliospores of rust fungi, Pucciniales Basidiomycota
Column of germinating teliospores of Cionothrix praelonga, Pucciniales Basidiomycota
Life cycle of Puccinia graminis on a grass, Pucciniales Basidiomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Septobasidium sp. on scale insects on bark of a living tree, Septobasidiales Basidiomycota
Fruiting body with basidia of Atractiella delectans, Atractiellales Basidiomycota
Hypha with a conidiogenous cell and a conidium of Hobsonia mirabilis, asexual form of Atractiellales Basidiomycota
Ascomycota
Phylogeny, subphyla of Ascomycota
Life cycle of Ascomycota, ascus
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Morphological groups, asexual fungi, imperfect fungi
Types of conidia, asexual fungi, imperfect fungi
Types of conidiogenesis, asexual fungi, imperfect fungi
Conidia, Ingoldian Hyphomycetes, staurospores, asexual fungi, imperfect fungi
Phylogeny of Pezizomycotina
Fruiting bodies of Ascomycota
Stilboid fungus, Helotiales, Ascomycota
Types of asci, Ascomycota
Morphological groups, orders, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Ascospores, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Pezizales, Ascomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fruiting bodies of Pezizales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Arthrobotrys superba, asexual, nematode trapping, Orbiliales, Ascomycota (drawing by R. Kirschner)
Fruiting bodies, Cyttariales, Helotiales, Leotiales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Fruiting bodies, Rhytismatales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Rhytisma acerinum with its asexual form Melasmia acerina, Rhytismatales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Hou Cheng-Lin; with permission.
Brasiliomyces malachrae, chasmothecium, Erysiphales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Erysiphales with its asexual form Oidium sp., Ascomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Conidiophores of Aspergillus sp., Penicillium sp., Eurotiales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Neurospora sp. with its asexual form Chrysonilia sp., Sordariales, Ascomycota
Based on Webster & Weber (2007), simplified.
Webster, J. & R.W.S. Weber. 2007. Introduction to fungi. Cambridge University Press.
Classification of Hypocreales, Clavicipitales, Clavicipitaceae, Ascomycota
Fruiting bodies of Hypocreales (without Clavicipitaceae), Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Life cycle of Hypocrea sp. with its asexual form Trichoderma sp., Hypocreales, Ascomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fruiting bodies of Clavicipitaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Claviceps purpurea with its asexual form Sphacelia sp., Clavicipitaceae, Hypocreales, Ascomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fungi hyperparasitic on insects on plants, Hypocreales, Ascomycota
Fruiting bodies of Xylariales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Fruiting bodies of Xylariales, Boliniales, Ascomycota
Fruiting bodies, ascospores, asexual forms, Xylariales, Ascomycota
Fruiting bodies of Meliolales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Meliolales, Ascomycota
Based on Rodríguez Justavino (2006).
Rodríguez Justavino, D. 2006. Meliolaceae aus Panama. Ph.D. thesis, University of Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fruiting bodies of Phyllachorales, Ascomycota
In collaboration with Tanja Trampe.
Life cycle of Phyllachorales, Ascomycota
Based on Trampe (2009).
Trampe, T. 2009. Neotropical tarspot fungi – exploration of Phyllachorales in Panama. Ph.D. thesis, University of Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fruiting bodies of Dothideomycetes, Ascomycota
Types of hamathecia, Dothideomycetes, Ascomycota
Based on Eriksson (1981).
Eriksson, O. 1981. The families of bitunicate ascomycetes. Opera Botanica 60: 1-209.
Asexual forms, Mycosphaerella, Mycosphaerellales, Ascomycota
Life cycle of Mycosphaerella sp. with its asexual form Pseudocercospora sp., Mycosphaerellales, Ascomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Fruiting body, ascus, ascospore, Myriangium sp., Myriangiales, Ascomycota
Asexual forms, Hyphomycetes, Pleosporales, Ascomycota
Asexual forms, Coelomycetes, Pleosporales, Ascomycota
Fruiting bodies, Asterinaceae, Microthyriales, Ascomycota
Based on Hofmann (2009).
Hofmann, T.A. 2009. Plant parasitic Asterinaceae and Microthyriaceae from the Neotropics (Panama). Ph.D. thesis, University of Frankfurt am Main, Germany.
Poliferation of ascogenous hypha, ascus, Ascomycota
Fruiting body, Antoniomyces loranthicola, Parmulariaceae, Ascomycota
Based on Inácio et al. (2012).
Inácio, C., K. Araúz & M. Piepenbring. 2012. A new genus of Parmulariaceae from Panama. Mycological Progress (published online 2011)
Life cycle of Laboulbenia sp., Laboulbeniales, Ascomycota
Based on Scheloske (1969).
Scheloske, H.-W. 1969. Beiträge zur Biologie, Ökologie und Systematik der Laboulbeniales (Ascomycetes). Parasitologische Schriftenreihe 19: 1-176.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Systematic groups including yeasts (written in red), Ascomycota, Basidiomycota
Life cycles of yeasts, Saccharomycetales, Schizosaccharomycetales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Taphrina deformans, Taphrinales, Ascomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Lichens
Interactions, green alga (green), fungal hypha, lichen, Lichenes
Systematic position of lichenized Ascomycota (written in green), Lichenes
Phylogenetic position of lichenized species among Ascomycota (simplified). Names written in green indicate groups of lichens. Names written with green and black letters refer to groups which include lichenized and non-lichenized species.
Growth forms of lichens, Lichenes
Anatomy of the thallus, green alga, cyanobacterium, lichen, Lichenes
Anatomy of the thallus, details, lichens, Lichenes
Asci and ascospores of lichens, Lichenes
Glomeromycota
Chlamydospores and siphonal hyphae of a sporocarp, Glomeromycota
Arbuscular mycorrhiza, Glomeromycota
In collaboration with Ingrid Kottke.
Zygomycota
Sporangiophores, sporangia, conidia, liberation of spores, Mucorales, Zygomycota
Zygospores of Mucorales, Zygomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Life cycle of Mucor sp., Mucorales, Zygomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Conidiogenous cells and conidia of Conidiobolus sp., Zygomycota
Chytridiomycota
Types of thalli of Chytridiomycota
Life cycle of Synchytrium endobioticum on potato, Chytridiomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, asexual, Chytridiomycota
Based on Longcore et al. (1999).
Longcore, J.E., A.P. Pessier & D.K. Nichols. 1999. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis gen. et sp. nov., a chytrid pathogenic to amphibians. Mycologia 91: 219-227.
Oomycetes
Phylogeny, simplified, Oomycota
Asexual structures of Saprolegniales, Oomycota
Based on Gäumann (1964).
Gäumann, E. 1964. Die Pilze, Grundzüge ihrer Entwicklungsgeschichte und Morphologie, 2nd edition. Birkhäuser, Basel, Stuttgart.
Life cycle of Saprolegnia sp., Saprolegniales, Oomycota
Sporangiophores of Phytophthora infestans and Pseudoperonospora cubensis, Peronosporales, Oomycota
Asexual structures of Saprolegniales, Albuginales, Peronosporales, Oomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Life cycle of Phytophthora infestans on potato, Peronosporales, Oomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Protistean fungi
Phylogeny of protistean fungi, slime molds, Myxomycota and other groups
Groups of mucilaginous fungi classified among protists. For orders, only the mycological names are cited. For classes and divisions, zoological names are cited first, and mycological names are added in quotation marks.
Morphological concepts, orders of Myxomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Life cycle of Stemonitis sp., Stemonitales, Myxomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Dictyostelium sp., asexual, Dictyosteliales, Myxomycota
Modified after unpublished diagrams by Franz Oberwinkler; with permission.
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Dictyostelium sp., sexual, Dictyosteliales, Myxomycota
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.
Life cycle of Plasmodiophora brassicae in cabbage, Plasmodiophoromycetes
Abbreviations: 1n = haploid, P! = plasmogamy, n+n = dikaryotic, K! = karyogamy, 2n = diploid, M! = meiosis
Red and blue circles represent haploid nuclei of different mating types, circles of both colors represent diploid nuclei.